Chemical bonds are the fundamental forces that hold molecules together, and understanding how they form is crucial to grasping the intricacies of chemistry. At the heart of chemical bonding lies the concept of atomic orbitals, which are the regions around an atom where an electron is likely to be found. In this article, we will delve into the world of atomic orbitals and explore the five primary ways they form chemical bonds.
Understanding Atomic Orbitals

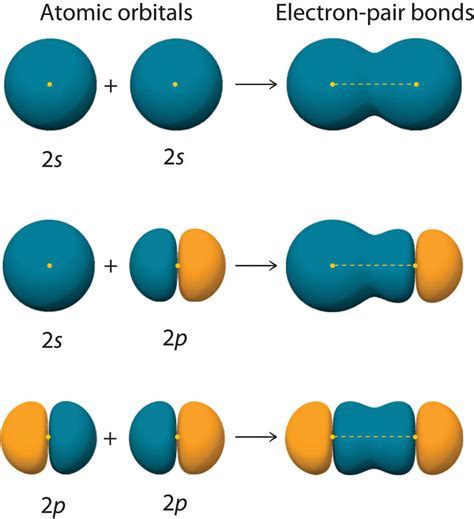
Atomic orbitals are the building blocks of chemical bonding. They are the regions around an atom where an electron is likely to be found, and they play a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of an element. The shape and orientation of atomic orbitals determine how they interact with other orbitals, which ultimately leads to the formation of chemical bonds.
The Five Primary Ways Orbitals Form Chemical Bonds
- Sigma (σ) Bonds
Sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent bond and are formed when two atomic orbitals overlap end-to-end. This type of bonding is typically found in molecules with a linear or bent shape. Sigma bonds are symmetrical around the bond axis and are formed by the overlap of s-orbitals, p-orbitals, or a combination of both.
- Pi (π) Bonds
Pi bonds are formed when two p-orbitals overlap side-by-side. This type of bonding is typically found in molecules with a planar or bent shape. Pi bonds are asymmetrical around the bond axis and are responsible for the formation of double and triple bonds.
- Delta (δ) Bonds
Delta bonds are formed when two d-orbitals overlap. This type of bonding is typically found in transition metal complexes and is responsible for the formation of strong covalent bonds.
- Hybridization
Hybridization occurs when two or more atomic orbitals combine to form a new orbital. This process allows atoms to form bonds that are stronger and more stable than those formed by individual orbitals. Hybridization is responsible for the formation of sp3, sp2, and sp hybrid orbitals, which are commonly found in organic molecules.
- Molecular Orbitals
Molecular orbitals are formed when atomic orbitals combine to form a new orbital that spans the entire molecule. This type of bonding is typically found in molecules with multiple atoms and is responsible for the formation of delocalized electrons.
Types of Chemical Bonds Formed by Orbitals

The five primary ways orbitals form chemical bonds lead to the formation of different types of chemical bonds, including:
- Covalent bonds: formed by the sharing of electrons between atoms
- Ionic bonds: formed by the transfer of electrons between atoms
- Metallic bonds: formed by the delocalization of electrons in metals
- Hydrogen bonds: formed by the attraction between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom
Factors Affecting Orbital Bonding
Several factors affect the formation of chemical bonds by orbitals, including:
- Electronegativity: the ability of an atom to attract electrons
- Atomic radius: the size of an atom
- Orbital shape: the shape and orientation of atomic orbitals
- Orbital energy: the energy of atomic orbitals
Conclusion

In conclusion, the five primary ways orbitals form chemical bonds are essential to understanding the intricacies of chemistry. By grasping the concepts of sigma, pi, delta, hybridization, and molecular orbitals, we can better comprehend the formation of chemical bonds and the properties of molecules. Whether you're a student of chemistry or simply interested in the subject, understanding orbitals and their role in chemical bonding is crucial to unlocking the secrets of the molecular world.
Take Action
Now that you've learned about the five primary ways orbitals form chemical bonds, take the next step and explore the world of chemistry further. Share this article with your friends and colleagues, and start a discussion about the importance of orbitals in chemical bonding.
What are atomic orbitals?
+Atomic orbitals are the regions around an atom where an electron is likely to be found.
What are the five primary ways orbitals form chemical bonds?
+The five primary ways orbitals form chemical bonds are sigma, pi, delta, hybridization, and molecular orbitals.
What factors affect the formation of chemical bonds by orbitals?
+Factors affecting the formation of chemical bonds by orbitals include electronegativity, atomic radius, orbital shape, and orbital energy.