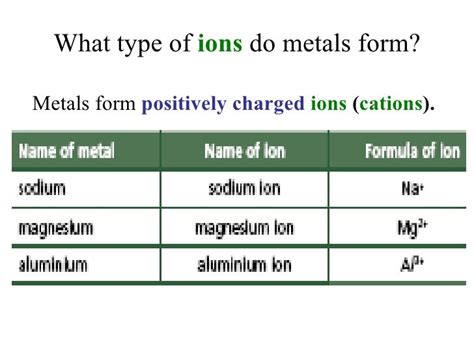
The world of chemistry is full of fascinating concepts, and one of the most interesting aspects is the behavior of metals in ionic reactions. Metals, which are typically shiny, malleable, and good conductors of electricity, have a unique way of forming ions that is distinct from nonmetals. Understanding how metals form ions is crucial in comprehending various chemical reactions and processes.
In this article, we will delve into the world of metal ions, exploring the types of ions they form, the reasons behind this behavior, and the implications of metal ions in various fields.
What Are Metal Ions?

Metal ions are atoms or groups of atoms that have gained or lost electrons to form a charged species. In the case of metals, they tend to lose electrons to form positively charged ions, known as cations. This process is called ionization. Metal ions are typically formed when a metal atom loses one or more electrons from its outermost energy level, resulting in a decrease in the number of electrons and an increase in the number of protons.
Why Do Metals Form Cations?
Metals form cations due to their atomic structure and the way they interact with other atoms. Metals have a tendency to lose electrons from their outermost energy level, which is often referred to as the valence shell. This is because the electrons in the valence shell are not strongly bound to the nucleus, making it easier for them to be removed.
When a metal atom loses an electron, it becomes a positively charged ion, known as a cation. This cation is then attracted to negatively charged ions, such as anions, to form a chemical bond. The formation of metal ions is an essential aspect of many chemical reactions, including acid-base reactions, redox reactions, and precipitation reactions.
Types of Metal Ions

There are several types of metal ions, each with its unique properties and characteristics. Some of the most common types of metal ions include:
- Alkali metal ions: These ions are formed by the alkali metals, which are located in Group 1 of the periodic table. Alkali metal ions are highly reactive and tend to form strong bonds with other ions.
- Alkaline earth metal ions: These ions are formed by the alkaline earth metals, which are located in Group 2 of the periodic table. Alkaline earth metal ions are less reactive than alkali metal ions but still tend to form strong bonds.
- Transition metal ions: These ions are formed by the transition metals, which are located in the d-block of the periodic table. Transition metal ions are known for their ability to form colored complexes and are often used as catalysts.
- Post-transition metal ions: These ions are formed by the post-transition metals, which are located in the p-block of the periodic table. Post-transition metal ions are generally less reactive than transition metal ions but still exhibit unique properties.
Properties of Metal Ions
Metal ions exhibit a range of properties, including:
- Charge: Metal ions have a positive charge, which is determined by the number of electrons lost during ionization.
- Size: Metal ions vary in size, depending on the number of electrons and protons present in the ion.
- Reactivity: Metal ions exhibit varying levels of reactivity, depending on their position in the periodic table and the number of electrons lost during ionization.
- Color: Some metal ions, particularly transition metal ions, exhibit unique colors due to the way they absorb and reflect light.
Applications of Metal Ions

Metal ions have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
- Catalysis: Metal ions are often used as catalysts in chemical reactions, where they facilitate the reaction without being consumed.
- Materials science: Metal ions are used to create a range of materials, including alloys, ceramics, and glasses.
- Biology: Metal ions play a crucial role in many biological processes, including enzyme function and protein structure.
- Medicine: Metal ions are used in various medical applications, including imaging agents and therapeutic agents.
Conclusion
In conclusion, metal ions are a fascinating aspect of chemistry, with a wide range of properties and applications. Understanding how metals form ions and the types of ions they form is essential in comprehending various chemical reactions and processes. From catalysis to biology, metal ions play a crucial role in many fields, and their unique properties make them an essential part of our daily lives.
What are metal ions?
+Metal ions are atoms or groups of atoms that have gained or lost electrons to form a charged species.
Why do metals form cations?
+Metals form cations due to their atomic structure and the way they interact with other atoms.
What are the types of metal ions?
+There are several types of metal ions, including alkali metal ions, alkaline earth metal ions, transition metal ions, and post-transition metal ions.
We hope you found this article informative and engaging. If you have any questions or would like to learn more about metal ions, please don't hesitate to comment below.