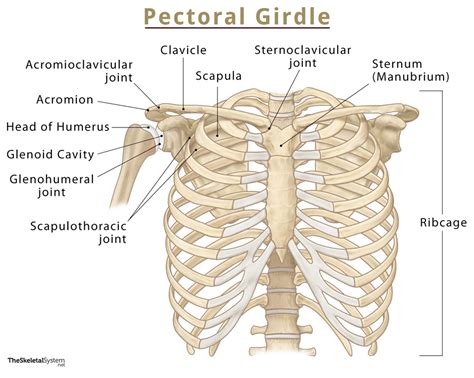
The human body is a complex and fascinating machine, comprising numerous bones, muscles, and organs that work in harmony to enable movement, support, and overall function. One of the most critical components of the skeletal system is the pectoral girdle, a group of bones that form the shoulder region. In this article, we will delve into the world of pectoral girdle bones, exploring their structure, functions, and importance in our daily lives.
The pectoral girdle, also known as the shoulder girdle, is a bony structure that connects the arm bones to the skeleton of the thorax, or chest region. It is composed of four bones: the scapula (shoulder blade), clavicle (collarbone), and the humerus (upper arm bone), as well as the sternum (breastbone). These bones work together to provide a wide range of motion, allowing us to perform various activities such as lifting, throwing, and even simple actions like brushing our teeth.
Scapula: The Foundation of the Pectoral Girdle

The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade, is a triangular bone that forms the posterior (rear) part of the pectoral girdle. It is a flat, curved bone that provides attachment points for numerous muscles, including the deltoids, trapezius, and rotator cuff muscles. The scapula plays a vital role in movements such as abduction (lifting the arm away from the body), adduction (bringing the arm towards the body), and rotation.
Functions of the Scapula
- Provides attachment points for muscles that control arm movements
- Acts as a pivot point for the arm, allowing for a wide range of motion
- Protects the underlying nerves and blood vessels
Clavicle: The Collarbone

The clavicle, or collarbone, is a long, slender bone that connects the scapula to the sternum. It is a vital part of the pectoral girdle, providing a strut-like function that helps to support the arm and shoulder region. The clavicle also serves as an attachment point for muscles such as the deltoids and trapezius.
Functions of the Clavicle
- Provides a strut-like function, supporting the arm and shoulder region
- Acts as an attachment point for muscles that control arm movements
- Helps to maintain the position of the scapula and arm
Humerus: The Upper Arm Bone

The humerus is a long, cylindrical bone that forms the upper arm. It is a vital part of the pectoral girdle, connecting the scapula to the forearm bones. The humerus provides attachment points for muscles such as the biceps and triceps, and plays a critical role in movements such as flexion (bending) and extension (straightening).
Functions of the Humerus
- Provides attachment points for muscles that control arm movements
- Acts as a pivot point for the arm, allowing for a wide range of motion
- Helps to maintain the position of the forearm and hand
Sternum: The Breastbone

The sternum, or breastbone, is a flat, narrow bone that forms the center of the chest region. It is a vital part of the pectoral girdle, connecting the clavicle to the ribcage. The sternum provides attachment points for muscles such as the pectoralis major, and plays a critical role in supporting the ribcage and maintaining the position of the heart and lungs.
Functions of the Sternum
- Provides attachment points for muscles that control chest movements
- Acts as a pivot point for the ribcage, allowing for expansion and contraction
- Helps to maintain the position of the heart and lungs
In conclusion, the pectoral girdle bones play a vital role in our daily lives, providing a wide range of motion and supporting the arm and shoulder region. Understanding the structure and functions of these bones can help us appreciate the complexity and beauty of the human body.
We hope you have found this article informative and engaging. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Don't forget to share this article with your friends and family, and follow us for more interesting content!
What is the pectoral girdle?
+The pectoral girdle is a bony structure that connects the arm bones to the skeleton of the thorax, or chest region. It is composed of four bones: the scapula, clavicle, humerus, and sternum.
What is the function of the scapula?
+The scapula provides attachment points for muscles that control arm movements, acts as a pivot point for the arm, and protects the underlying nerves and blood vessels.
What is the function of the clavicle?
+The clavicle provides a strut-like function, supporting the arm and shoulder region, acts as an attachment point for muscles that control arm movements, and helps to maintain the position of the scapula and arm.