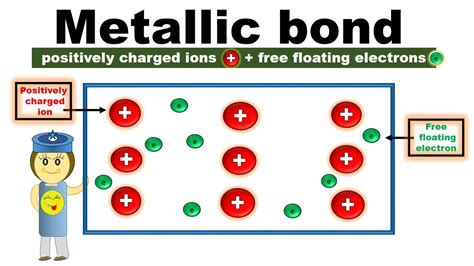
Metallic bonds are a type of chemical bond that is typically found in metals and metal alloys. These bonds are responsible for the unique properties of metals, such as their high electrical and thermal conductivity, malleability, and ductility. In this article, we will delve into the world of metallic bonds, exploring what they are, how they are formed, and their characteristics.

What are Metallic Bonds?
Metallic bonds are a type of delocalized covalent bond, which means that the electrons are not localized between two specific atoms, but are instead free to move throughout the metal lattice. This delocalization of electrons is what gives metals their unique properties. In a metallic bond, the electrons are not paired with specific atoms, but are instead part of a "sea" of electrons that surrounds the positively charged metal ions.
How are Metallic Bonds Formed?
Metallic bonds are formed when a metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion, known as a cation. This process is known as ionization. The electrons that are lost by the metal atom are then delocalized, meaning they are free to move throughout the metal lattice. The delocalized electrons are attracted to the positively charged metal ions, which holds them together and forms a metallic bond.
Characteristics of Metallic Bonds
Metallic bonds have several characteristics that distinguish them from other types of chemical bonds. Some of the key characteristics of metallic bonds include:
-
High Electrical Conductivity
Metallic bonds allow electrons to move freely throughout the metal lattice, which makes metals good conductors of electricity. This is why metals are often used in electrical wiring and other applications where high electrical conductivity is required.
-
High Thermal Conductivity
Metallic bonds also allow heat to be transferred efficiently through the metal lattice, which makes metals good conductors of heat. This is why metals are often used in cookware and other applications where high thermal conductivity is required.
-
Malleability and Ductility
Metallic bonds are relatively weak compared to other types of chemical bonds, which makes metals malleable and ductile. This means that metals can be easily shaped and molded without breaking.
-
High Melting Points
Metallic bonds require a significant amount of energy to break, which is why metals have high melting points. This is why metals are often used in high-temperature applications, such as in engines and other machinery.

Types of Metallic Bonds
There are several types of metallic bonds, including:
-
Polycationic Metallic Bonds
In polycationic metallic bonds, multiple metal ions are bonded together by a single delocalized electron. This type of bond is typically found in metals such as sodium and potassium.
-
Polyanionic Metallic Bonds
In polyanionic metallic bonds, multiple metal ions are bonded together by multiple delocalized electrons. This type of bond is typically found in metals such as magnesium and calcium.
-
Transition Metal Bonds
Transition metal bonds are a type of metallic bond that is found in transition metals, such as iron and copper. These bonds are characterized by the presence of partially filled d orbitals, which allows for the delocalization of electrons.

Applications of Metallic Bonds
Metallic bonds have a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
-
Electrical Wiring
Metallic bonds are used in electrical wiring due to their high electrical conductivity.
-
Cookware
Metallic bonds are used in cookware due to their high thermal conductivity.
-
Engines and Machinery
Metallic bonds are used in engines and other machinery due to their high melting points and strength.
-
Medical Applications
Metallic bonds are used in medical applications, such as in implants and surgical instruments, due to their biocompatibility and strength.

In conclusion, metallic bonds are a unique type of chemical bond that is found in metals and metal alloys. These bonds are responsible for the unique properties of metals, such as their high electrical and thermal conductivity, malleability, and ductility. By understanding the characteristics and applications of metallic bonds, we can better appreciate the importance of these bonds in our daily lives.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of metallic bonds. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
What is the difference between metallic bonds and ionic bonds?
+Metallic bonds are a type of delocalized covalent bond, while ionic bonds are a type of electrostatic attraction between oppositely charged ions.
What are some examples of metals that exhibit metallic bonds?
+Examples of metals that exhibit metallic bonds include sodium, potassium, magnesium, and calcium.
What are some applications of metallic bonds?
+Metallic bonds have a wide range of applications, including electrical wiring, cookware, engines and machinery, and medical applications.