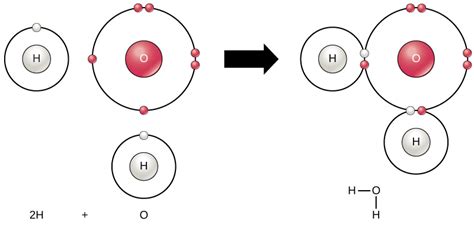
Oxygen is a highly reactive element that readily forms ions in chemical reactions. In its most common form, oxygen reacts with other elements to form oxides, which are compounds that contain oxygen in the form of an ion. The ion formed by oxygen in chemical reactions is the oxide ion, also known as the oxygen anion.
When oxygen gains two electrons, it forms a negatively charged ion with a charge of -2. This ion is denoted by the symbol O2- and is commonly referred to as the oxide ion. The formation of the oxide ion is a result of the oxygen atom's tendency to attract electrons, which is known as electronegativity. Oxygen has a high electronegativity value, which means that it has a strong tendency to attract electrons towards itself.
The oxide ion is a common ion in many chemical compounds, including metal oxides, non-metal oxides, and oxyanions. Metal oxides are compounds that consist of a metal cation bonded to one or more oxide ions. Examples of metal oxides include iron(III) oxide (Fe2O3), aluminum oxide (Al2O3), and titanium dioxide (TiO2). Non-metal oxides, on the other hand, are compounds that consist of a non-metal cation bonded to one or more oxide ions. Examples of non-metal oxides include carbon dioxide (CO2), sulfur trioxide (SO3), and phosphorus pentoxide (P2O5).
Oxyanions are compounds that consist of an oxide ion bonded to one or more other elements. Examples of oxyanions include the sulfate ion (SO42-), the nitrate ion (NO3-), and the phosphate ion (PO43-). These ions are commonly found in acidic environments and play an important role in many chemical reactions.
The formation of the oxide ion is an important aspect of many chemical reactions, including combustion reactions, acid-base reactions, and redox reactions. Combustion reactions involve the reaction of a substance with oxygen, resulting in the formation of heat and light. Acid-base reactions involve the transfer of electrons between an acid and a base, resulting in the formation of ions, including the oxide ion. Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between two substances, resulting in the formation of ions, including the oxide ion.

Formation of Oxygen Ions in Chemical Reactions
Oxygen ions are formed in chemical reactions through a variety of mechanisms, including:
- Electron transfer: Oxygen can gain or lose electrons to form ions. When oxygen gains two electrons, it forms a negatively charged oxide ion.
- Proton transfer: Oxygen can also form ions through the transfer of protons (H+ ions). For example, when oxygen reacts with water, it forms a hydroxide ion (OH-).
- Covalent bonding: Oxygen can form ions through covalent bonding with other elements. For example, when oxygen reacts with carbon, it forms a carbonate ion (CO32-).
The formation of oxygen ions is an important aspect of many chemical reactions, including:
- Combustion reactions: Combustion reactions involve the reaction of a substance with oxygen, resulting in the formation of heat and light.
- Acid-base reactions: Acid-base reactions involve the transfer of electrons between an acid and a base, resulting in the formation of ions, including the oxide ion.
- Redox reactions: Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between two substances, resulting in the formation of ions, including the oxide ion.
Examples of Oxygen Ions in Chemical Reactions
- Sodium oxide: Sodium oxide (Na2O) is a compound that consists of sodium ions bonded to oxide ions.
- Calcium carbonate: Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) is a compound that consists of calcium ions bonded to carbonate ions.
- Sulfuric acid: Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is a compound that consists of hydrogen ions bonded to sulfate ions.

Properties of Oxygen Ions
Oxygen ions have several important properties, including:
- Charge: Oxygen ions have a charge of -2, which means that they are negatively charged.
- Electronegativity: Oxygen ions have a high electronegativity value, which means that they have a strong tendency to attract electrons.
- Reactivity: Oxygen ions are highly reactive, which means that they readily participate in chemical reactions.
- Solubility: Oxygen ions are highly soluble in water, which means that they can easily dissolve in aqueous solutions.
Importance of Oxygen Ions in Biological Systems
Oxygen ions play an important role in many biological systems, including:
- Respiration: Oxygen ions are involved in the process of respiration, which is the process by which cells generate energy from glucose.
- Photosynthesis: Oxygen ions are involved in the process of photosynthesis, which is the process by which plants generate energy from sunlight.
- Cell signaling: Oxygen ions are involved in cell signaling, which is the process by which cells communicate with each other.

Conclusion
In conclusion, oxygen ions are an important aspect of many chemical reactions, including combustion reactions, acid-base reactions, and redox reactions. The formation of oxygen ions is an important aspect of many biological systems, including respiration, photosynthesis, and cell signaling. Understanding the properties and behavior of oxygen ions is essential for understanding many chemical and biological processes.

We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of oxygen ions and their role in chemical reactions. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to leave them in the section below.
What is the charge of an oxygen ion?
+The charge of an oxygen ion is -2.
What is the electronegativity value of oxygen ions?
+The electronegativity value of oxygen ions is high, which means that they have a strong tendency to attract electrons.
What is the role of oxygen ions in biological systems?
+Oxygen ions play an important role in many biological systems, including respiration, photosynthesis, and cell signaling.