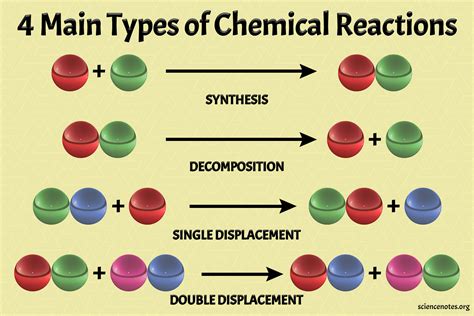
The world of chemical reactions is a complex and fascinating one, with various reactant pairs coming together to form products through different processes. Understanding these reactant pairs and their interactions is crucial in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. In this article, we will explore the top 5 reactant pairs that form products easily, discussing their characteristics, reaction mechanisms, and significance in various applications.

1. Sodium and Chlorine: A Highly Reactive Pair
Sodium (Na) and chlorine (Cl2) are a highly reactive pair, forming sodium chloride (NaCl), commonly known as table salt, through a single displacement reaction. This reaction is highly exothermic, releasing a significant amount of energy in the form of heat and light.
Na (s) + Cl2 (g) → NaCl (s)
The reaction occurs when sodium, a highly electropositive metal, reacts with chlorine gas, a highly electronegative nonmetal. The reaction is highly favorable due to the large difference in electronegativity between the two elements.

Applications of Sodium Chloride
Sodium chloride has numerous applications in various industries, including:
- Food preservation: Sodium chloride is widely used as a food preservative, inhibiting the growth of microorganisms and extending the shelf life of food products.
- Pharmaceuticals: Sodium chloride is used as an excipient in various pharmaceutical applications, including tablets, capsules, and injections.
- Industrial processes: Sodium chloride is used in various industrial processes, including the manufacture of paper, dyes, and textiles.
2. Calcium Carbonate and Hydrochloric Acid: A Neutralization Reaction
Calcium carbonate (CaCO3) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) are a reactant pair that form calcium chloride (CaCl2), water (H2O), and carbon dioxide (CO2) through a neutralization reaction.
CaCO3 (s) + 2HCl (aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g)
The reaction occurs when calcium carbonate, a weak base, reacts with hydrochloric acid, a strong acid. The reaction is highly favorable due to the large difference in pH between the two reactants.

Applications of Calcium Chloride
Calcium chloride has numerous applications in various industries, including:
- De-icing: Calcium chloride is widely used as a de-icing agent, lowering the freezing point of water and preventing ice formation on roads and surfaces.
- Pharmaceuticals: Calcium chloride is used as an excipient in various pharmaceutical applications, including tablets, capsules, and injections.
- Food industry: Calcium chloride is used as a food additive, enhancing the texture and flavor of various food products.
3. Ammonia and Nitric Acid: A Neutralization Reaction
Ammonia (NH3) and nitric acid (HNO3) are a reactant pair that form ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) through a neutralization reaction.
NH3 (g) + HNO3 (aq) → NH4NO3 (s)
The reaction occurs when ammonia, a weak base, reacts with nitric acid, a strong acid. The reaction is highly favorable due to the large difference in pH between the two reactants.

Applications of Ammonium Nitrate
Ammonium nitrate has numerous applications in various industries, including:
- Fertilizers: Ammonium nitrate is widely used as a fertilizer, providing nitrogen and other essential nutrients to crops.
- Explosives: Ammonium nitrate is used in the manufacture of explosives, including dynamite and other blasting agents.
- Pharmaceuticals: Ammonium nitrate is used as an excipient in various pharmaceutical applications, including tablets, capsules, and injections.
4. Copper and Sulfuric Acid: A Redox Reaction
Copper (Cu) and sulfuric acid (H2SO4) are a reactant pair that form copper sulfate (CuSO4) and hydrogen gas (H2) through a redox reaction.
Cu (s) + 2H2SO4 (aq) → CuSO4 (aq) + 2H2 (g)
The reaction occurs when copper, a metal, reacts with sulfuric acid, an oxidizing agent. The reaction is highly favorable due to the large difference in electronegativity between the two reactants.

Applications of Copper Sulfate
Copper sulfate has numerous applications in various industries, including:
- Agriculture: Copper sulfate is used as a pesticide, fungicide, and algicide in agriculture, controlling pests and diseases in crops.
- Pharmaceuticals: Copper sulfate is used as an excipient in various pharmaceutical applications, including tablets, capsules, and injections.
- Industrial processes: Copper sulfate is used in various industrial processes, including the manufacture of paper, dyes, and textiles.
5. Potassium and Water: A Highly Exothermic Reaction
Potassium (K) and water (H2O) are a reactant pair that form potassium hydroxide (KOH) and hydrogen gas (H2) through a highly exothermic reaction.
2K (s) + 2H2O (l) → 2KOH (aq) + H2 (g)
The reaction occurs when potassium, a highly electropositive metal, reacts with water, a polar solvent. The reaction is highly favorable due to the large difference in electronegativity between the two reactants.

Applications of Potassium Hydroxide
Potassium hydroxide has numerous applications in various industries, including:
- Soap manufacturing: Potassium hydroxide is used in the manufacture of soap, providing a strong alkaline solution for saponification reactions.
- Pharmaceuticals: Potassium hydroxide is used as an excipient in various pharmaceutical applications, including tablets, capsules, and injections.
- Industrial processes: Potassium hydroxide is used in various industrial processes, including the manufacture of paper, dyes, and textiles.
We hope you've enjoyed this in-depth look at the top 5 reactant pairs that form products easily. Each of these reactant pairs has unique characteristics and applications, highlighting the diversity and complexity of chemical reactions.
Now, we'd love to hear from you! What are your favorite reactant pairs, and how do you use them in your work or daily life? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!
What is a reactant pair?
+A reactant pair is a combination of two substances that react with each other to form a product or products.
What are some common types of chemical reactions?
+Some common types of chemical reactions include synthesis reactions, decomposition reactions, single displacement reactions, double displacement reactions, and combustion reactions.
How do I determine the products of a chemical reaction?
+To determine the products of a chemical reaction, you can use the reaction equation, balancing the equation to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is conserved.