The world of chemistry is full of fascinating phenomena, and one of the most intriguing is the instantaneous formation of two new compounds through a chemical reaction. This process, known as a "binary reaction," is a fundamental concept in chemistry that has far-reaching implications for various fields, including pharmaceuticals, materials science, and environmental studies.
In a binary reaction, two reactants combine to form two new products, often with distinct properties and characteristics. This process is instantaneous, meaning it occurs rapidly, often in a matter of seconds or even milliseconds. The speed and efficiency of binary reactions make them a crucial aspect of many chemical processes, from the synthesis of complex molecules to the degradation of pollutants.
Understanding Binary Reactions

To comprehend the principles of binary reactions, it's essential to delve into the world of chemical kinetics. Chemical kinetics is the study of the rates and mechanisms of chemical reactions, including binary reactions. By understanding the kinetics of binary reactions, scientists can optimize reaction conditions, predict product yields, and design more efficient chemical processes.
The Mechanisms of Binary Reactions
Binary reactions involve a complex interplay of molecular interactions, which can be broadly classified into two categories: concerted and stepwise mechanisms. Concerted mechanisms involve a single, simultaneous step, where the reactants combine to form products in a single reaction coordinate. Stepwise mechanisms, on the other hand, involve multiple steps, where the reactants form intermediate species before eventually producing the final products.
Types of Binary Reactions

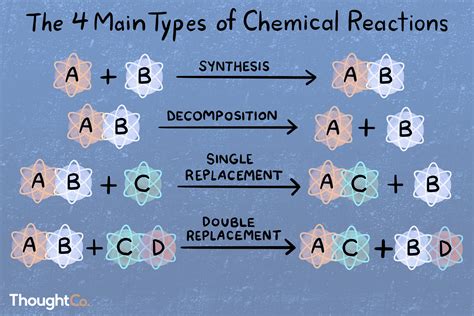
Binary reactions can be categorized into several types, each with distinct characteristics and applications:
- Synthesis reactions: These reactions involve the combination of two reactants to form a new compound. Synthesis reactions are commonly used in pharmaceuticals, materials science, and organic synthesis.
- Decomposition reactions: These reactions involve the breakdown of a single reactant into two or more products. Decomposition reactions are often used in environmental studies, where they can help break down pollutants.
- Substitution reactions: These reactions involve the replacement of one functional group with another. Substitution reactions are commonly used in organic synthesis and materials science.
Applications of Binary Reactions
Binary reactions have far-reaching implications for various fields, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Binary reactions are used to synthesize complex molecules, such as antibiotics and cancer medications.
- Materials science: Binary reactions are used to develop new materials, such as nanomaterials and polymers.
- Environmental studies: Binary reactions are used to break down pollutants and understand environmental processes.
Challenges and Limitations of Binary Reactions

While binary reactions are a powerful tool for chemists, they also present several challenges and limitations:
- Scalability: Binary reactions can be difficult to scale up, as the reaction conditions and yields may vary depending on the size of the reaction.
- Selectivity: Binary reactions often require precise control over reaction conditions to achieve high selectivity and minimize side reactions.
- Stability: Binary reactions can be sensitive to temperature, pressure, and other environmental factors, which can affect the stability of the reaction.
Future Directions of Binary Reactions
Despite the challenges and limitations, binary reactions continue to be an active area of research, with scientists exploring new applications and techniques:
- Microreactors: Microreactors are small-scale reactors that can be used to study binary reactions under controlled conditions.
- Flow chemistry: Flow chemistry involves the continuous flow of reactants through a reactor, which can improve reaction efficiency and scalability.
- Computational modeling: Computational modeling can be used to simulate binary reactions and predict reaction outcomes.
What is a binary reaction?
+A binary reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the combination of two reactants to form two new products.
What are the applications of binary reactions?
+Binary reactions have applications in pharmaceuticals, materials science, environmental studies, and other fields.
What are the challenges of binary reactions?
+Binary reactions can be challenging to scale up, require precise control over reaction conditions, and can be sensitive to environmental factors.
In conclusion, binary reactions are a fundamental concept in chemistry that has far-reaching implications for various fields. By understanding the mechanisms, types, and applications of binary reactions, scientists can develop new technologies and improve existing processes. While challenges and limitations exist, ongoing research and advancements in techniques are expanding the potential of binary reactions.