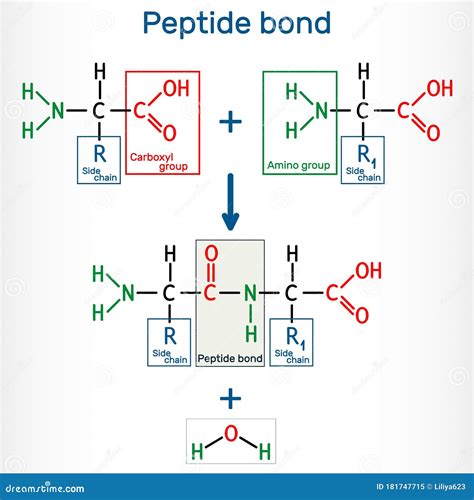
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and when two or more amino acids are linked together through a peptide bond, they form a peptide or a protein. This bond is a crucial aspect of protein structure and function, and understanding how it forms is essential for appreciating the complexity of biological systems.
The peptide bond is a type of covalent bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid. This bond is formed through a dehydration reaction, where a molecule of water is released as the two amino acids come together. The resulting bond is strong and stable, allowing proteins to maintain their complex structures and perform a wide range of biological functions.

Peptide Bond Formation
The formation of a peptide bond is a complex process that involves several steps. The first step is the activation of the carboxyl group of one amino acid, which is typically achieved through the addition of energy in the form of ATP. This energy is used to drive the reaction forward and ensure that the bond forms correctly.
Once the carboxyl group is activated, it is able to react with the amino group of another amino acid. This reaction involves the transfer of a molecule of water, which is released as the two amino acids come together. The resulting bond is a peptide bond, which is characterized by a planar, trans configuration.

Types of Peptide Bonds
There are several types of peptide bonds, each with its own unique characteristics. The most common type of peptide bond is the α-peptide bond, which forms between the α-amino group of one amino acid and the α-carboxyl group of another amino acid. This type of bond is the most common in biological systems and is responsible for the formation of proteins.
Other types of peptide bonds include the β-peptide bond, which forms between the β-amino group of one amino acid and the β-carboxyl group of another amino acid. This type of bond is less common in biological systems but is still important for the formation of certain proteins.

Importance of Peptide Bonds
Peptide bonds are essential for the formation and function of proteins, which are the building blocks of all living organisms. Proteins perform a wide range of biological functions, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, replicating DNA, and responding to stimuli.
The strength and stability of peptide bonds allow proteins to maintain their complex structures and perform their biological functions. Without peptide bonds, proteins would not be able to form the complex structures that are necessary for life.

Peptide Bond Breakage
Peptide bonds can be broken through a process called hydrolysis, which involves the addition of water to the bond. This process is the reverse of peptide bond formation and is catalyzed by enzymes called peptidases.
Peptide bond breakage is an important process in biological systems, as it allows proteins to be degraded and recycled. This process is also important for the digestion of proteins in the gut, where peptidases break down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids that can be absorbed by the body.

Applications of Peptide Bonds
Peptide bonds have a wide range of applications in biology, medicine, and industry. In biology, peptide bonds are used to study protein structure and function, and to develop new therapeutic agents.
In medicine, peptide bonds are used to develop new drugs and therapies, such as peptide-based vaccines and peptide-based cancer treatments. Peptide bonds are also used in the development of biomaterials and biosensors.

Future Directions
The study of peptide bonds is an active area of research, with many scientists working to develop new methods for forming and breaking peptide bonds. This research has the potential to lead to the development of new therapeutic agents and biomaterials.
In addition, the study of peptide bonds is also important for understanding the origins of life on Earth. Scientists believe that peptide bonds may have played a key role in the formation of the first living cells, and studying these bonds may provide insights into the origins of life.

In conclusion, peptide bonds are a crucial aspect of protein structure and function, and understanding how they form and break is essential for appreciating the complexity of biological systems. The study of peptide bonds has many applications in biology, medicine, and industry, and is an active area of research that continues to evolve and expand our knowledge of the natural world.
We encourage you to share your thoughts on the importance of peptide bonds in the comments section below. How do you think the study of peptide bonds will impact our understanding of biology and medicine in the future?
What is a peptide bond?
+A peptide bond is a type of covalent bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another amino acid.
How are peptide bonds formed?
+Peptide bonds are formed through a dehydration reaction, where a molecule of water is released as the two amino acids come together.
What is the importance of peptide bonds in biology?
+Peptide bonds are essential for the formation and function of proteins, which are the building blocks of all living organisms.