Tax season is upon us, and with it comes the flurry of forms and paperwork that can be overwhelming to navigate. One of the most important forms for individuals with investment income is the 1099 form from Truist, a leading financial services company. If you're among the many people who receive a Truist 1099 form each year, you may be wondering what it means and how to understand the information it contains. In this article, we'll break down the 5 ways to understand your Truist 1099 form, so you can confidently tackle tax season.
What is a 1099 Form?
Before we dive into the specifics of the Truist 1099 form, let's quickly review what a 1099 form is in general. A 1099 form is a tax document that reports various types of income, such as interest, dividends, capital gains, and freelance work, to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). The form is used by banks, brokerages, and other financial institutions to report income earned by their customers. In the case of Truist, the 1099 form reports income earned on investments held through the company.
Understanding Your Truist 1099 Form
Now that we've covered the basics, let's move on to the 5 ways to understand your Truist 1099 form:
1. Review the Different Types of 1099 Forms from Truist

Truist issues several types of 1099 forms, each reporting different types of income. The most common types of 1099 forms from Truist include:
- 1099-INT: Reports interest income earned on investments, such as CDs, savings accounts, and bonds.
- 1099-DIV: Reports dividend income earned on stock investments.
- 1099-B: Reports capital gains and losses from the sale of investments, such as stocks, bonds, and mutual funds.
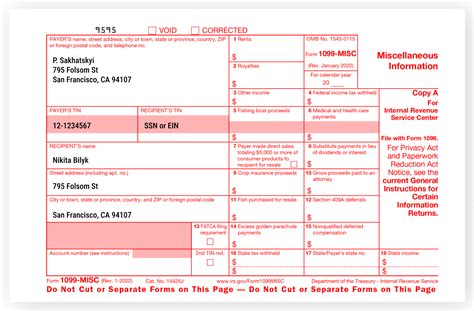
- 1099-MISC: Reports miscellaneous income, such as freelance work or rent.
Understanding which type of 1099 form you received from Truist will help you navigate the information it contains.
2. Understand the Boxes and Sections on the 1099 Form
Each 1099 form from Truist contains several boxes and sections that report different types of income. Here's a breakdown of what you can expect to find on each type of 1099 form:
- Box 1: Reports the total amount of interest or dividend income earned.
- Box 2: Reports the total amount of capital gains or losses.
- Box 3: Reports the total amount of miscellaneous income.
- Section 2: Reports the payer's information, including their name, address, and tax identification number.
Understanding the different boxes and sections on the 1099 form will help you accurately report your income on your tax return.
3. Reconcile Your 1099 Form with Your Investment Statements

To ensure the accuracy of your 1099 form, it's a good idea to reconcile the information with your investment statements. Here's how:
- Compare the interest, dividend, and capital gains income reported on your 1099 form with the income reported on your investment statements.
- Verify that the payer's information, including their name and tax identification number, matches the information on your investment statements.
Reconciling your 1099 form with your investment statements will help you catch any errors or discrepancies that may have occurred.
4. Understand the Tax Implications of Your 1099 Form
Your 1099 form from Truist will report income that is subject to taxation. Here's what you need to know about the tax implications:
- Interest income: Reported on Line 2a of Form 1040.
- Dividend income: Reported on Line 3a of Form 1040.
- Capital gains: Reported on Schedule D of Form 1040.
- Miscellaneous income: Reported on Line 21 of Form 1040.
Understanding the tax implications of your 1099 form will help you accurately report your income and claim any deductions or credits you may be eligible for.
5. Seek Professional Help if You're Unsure

If you're unsure about any aspect of your 1099 form from Truist, don't hesitate to seek professional help. Here are some options:
- Consult with a tax professional, such as a certified public accountant (CPA) or enrolled agent (EA).
- Contact Truist customer support for assistance with understanding your 1099 form.
- Visit the IRS website for guidance on reporting income from a 1099 form.
Seeking professional help will ensure that you accurately report your income and take advantage of any deductions or credits you may be eligible for.
Additional Tips and Reminders
Here are some additional tips and reminders to keep in mind when understanding your Truist 1099 form:
- Make sure to report all income earned from investments, even if you don't receive a 1099 form.
- Keep accurate records of your investment income and expenses to support your tax return.
- Don't hesitate to reach out to Truist or a tax professional if you have questions or concerns about your 1099 form.
Conclusion
Understanding your Truist 1099 form is crucial for accurately reporting your income and taking advantage of any deductions or credits you may be eligible for. By following the 5 ways outlined in this article, you'll be well on your way to confidently navigating tax season. Remember to seek professional help if you're unsure about any aspect of your 1099 form, and don't hesitate to reach out to Truist or a tax professional if you have questions or concerns.
What's Next?
Now that you've read this article, take the next step by:
- Reviewing your Truist 1099 form to understand the different types of income reported.
- Reconciling your 1099 form with your investment statements to ensure accuracy.
- Seeking professional help if you're unsure about any aspect of your 1099 form.
Share your thoughts and questions in the comments section below, and don't forget to share this article with friends and family who may be struggling to understand their Truist 1099 form.
What is a 1099 form from Truist?
+A 1099 form from Truist is a tax document that reports various types of income, such as interest, dividends, capital gains, and freelance work, to the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
What types of 1099 forms does Truist issue?
+Truist issues several types of 1099 forms, including 1099-INT, 1099-DIV, 1099-B, and 1099-MISC.
How do I reconcile my 1099 form with my investment statements?
+Compare the interest, dividend, and capital gains income reported on your 1099 form with the income reported on your investment statements. Verify that the payer's information, including their name and tax identification number, matches the information on your investment statements.