The human body is a complex and fascinating machine, comprising 206 bones that work together to provide support, protection, and movement. At the center of this intricate system lies the axial skeleton, a vital component that plays a crucial role in our overall anatomy. In this article, we will delve into the three main components of the axial skeleton, exploring their functions, structures, and importance in maintaining our overall health and well-being.
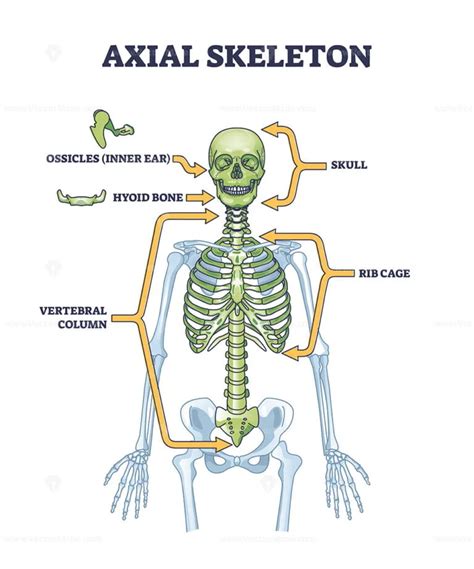
The axial skeleton is the central axis of the body, extending from the skull to the tailbone. It serves as the foundation for the entire skeletal system, providing a framework for the muscles, organs, and other tissues to attach and function properly. Without a properly functioning axial skeleton, our bodies would be unable to maintain posture, facilitate movement, or protect the delicate internal organs.

Skull: The Uppermost Component
The skull is the uppermost component of the axial skeleton, comprising the cranium and the face. The cranium, also known as the braincase, is a bony structure that encloses and protects the brain, while the face is composed of 14 bones that fuse together to form the nasal cavity, orbits, and jaw. The skull serves several critical functions, including:
- Protecting the brain and sensory organs (eyes, ears, and nose)
- Providing attachment points for muscles of facial expression and mastication (chewing)
- Forming the nasal and oral cavities for breathing and eating
Vertebral Column: The Central Component
The vertebral column, also known as the spine, is the central component of the axial skeleton, extending from the base of the skull to the tailbone. It is composed of 33 vertebrae, which are divided into five regions: cervical (neck), thoracic (chest), lumbar (lower back), sacrum (pelvis), and coccyx (tailbone). The vertebral column serves several essential functions, including:
- Providing support and stability for the body
- Facilitating movement and flexibility
- Protecting the spinal cord and nerve roots
Ribcage and Sternum: The Thoracic Component
The ribcage and sternum form the thoracic component of the axial skeleton, which is responsible for protecting the heart and lungs. The ribcage is composed of 12 pairs of ribs, which are attached to the thoracic vertebrae and the sternum (breastbone). The ribcage serves several critical functions, including:
- Protecting the heart and lungs
- Providing attachment points for muscles of respiration and movement
- Forming the thoracic cavity for breathing
Conclusion
In conclusion, the axial skeleton is a vital component of the human body, comprising the skull, vertebral column, and ribcage and sternum. Each of these components plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being, from protecting the brain and internal organs to facilitating movement and supporting the body. By understanding the functions and structures of the axial skeleton, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the intricate complexity of the human body and the importance of maintaining a healthy and functioning skeletal system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main function of the axial skeleton?
+The main function of the axial skeleton is to provide support, protection, and movement for the body.
What are the three main components of the axial skeleton?
+The three main components of the axial skeleton are the skull, vertebral column, and ribcage and sternum.
What is the function of the vertebral column?
+The vertebral column provides support and stability for the body, facilitates movement and flexibility, and protects the spinal cord and nerve roots.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the axial skeleton and its importance in the human body. If you have any further questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.