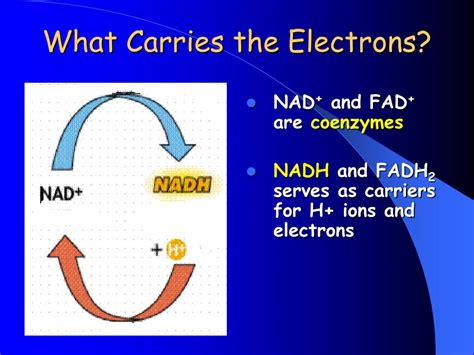
The process of glycolysis is a crucial step in cellular respiration, where glucose is converted into pyruvate, generating energy for the cell. One of the key players in this process is NADH (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), a coenzyme that plays a vital role in the transfer of electrons. In this article, we will delve into the world of NADH, exploring its reduced form and its significance in glycolysis.
What is NADH?
NADH is a coenzyme that consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine base, while the other contains nicotinamide. NADH is the reduced form of NAD+ (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide), which is the oxidized form. The conversion between NAD+ and NADH is a reversible process, with NADH being the reduced form and NAD+ being the oxidized form.
The Role of NADH in Glycolysis
Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, generating energy for the cell. During this process, NAD+ is reduced to form NADH, which plays a crucial role in the transfer of electrons. NADH is the electron acceptor that facilitates the conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
In this reaction, NAD+ is reduced to form NADH, while glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is converted to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.

The Reduced Form of NADH
The reduced form of NADH is characterized by the presence of two electrons, which are transferred from the reduced substrate to the coenzyme. This transfer of electrons reduces the NAD+ to form NADH, which is then used to generate energy for the cell.
The reduced form of NADH is essential for the proper functioning of glycolysis. Without NADH, the conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate would not be possible, and the cell would not be able to generate energy from glucose.
The Significance of NADH in Cellular Respiration
NADH plays a crucial role in cellular respiration, where it is used to generate energy for the cell. The electrons transferred to NADH during glycolysis are passed on to the electron transport chain, where they are used to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
The significance of NADH in cellular respiration cannot be overstated. Without NADH, the cell would not be able to generate energy from glucose, and the entire process of cellular respiration would come to a halt.
NADH and the Electron Transport Chain
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes located in the mitochondrial inner membrane. It is here that the electrons transferred to NADH during glycolysis are passed on to generate ATP.
The electron transport chain consists of four protein complexes, each with a specific role to play in the transfer of electrons. The electrons transferred to NADH are passed on to complex I, which then transfers them to coenzyme Q. From here, the electrons are passed on to complex III, and finally to complex IV, where they are used to generate ATP.

The Benefits of NADH
NADH has several benefits, including:
- Energy production: NADH plays a crucial role in the production of energy for the cell.
- Antioxidant properties: NADH has antioxidant properties, which help to protect the cell from damage caused by free radicals.
- Neuroprotection: NADH has been shown to have neuroprotective effects, where it helps to protect the brain from damage caused by oxidative stress.
NADH Deficiency**
A deficiency in NADH can have serious consequences for the cell. Without NADH, the cell would not be able to generate energy from glucose, and the entire process of cellular respiration would come to a halt.
A deficiency in NADH can be caused by a number of factors, including:
- Genetic mutations: Genetic mutations can affect the production of NADH, leading to a deficiency.
- Aging: NADH levels decline with age, which can lead to a deficiency.
- Diet: A diet that is deficient in nutrients can lead to a deficiency in NADH.

Conclusion
In conclusion, NADH plays a crucial role in the process of glycolysis, where it is used to generate energy for the cell. The reduced form of NADH is essential for the proper functioning of glycolysis, and a deficiency in NADH can have serious consequences for the cell.
We hope that this article has provided you with a better understanding of NADH and its role in glycolysis. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
What is the role of NADH in glycolysis?
+NADH plays a crucial role in the process of glycolysis, where it is used to generate energy for the cell. It is the electron acceptor that facilitates the conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate.
What is the reduced form of NADH?
+The reduced form of NADH is characterized by the presence of two electrons, which are transferred from the reduced substrate to the coenzyme.
What are the benefits of NADH?
+NADH has several benefits, including energy production, antioxidant properties, and neuroprotection.