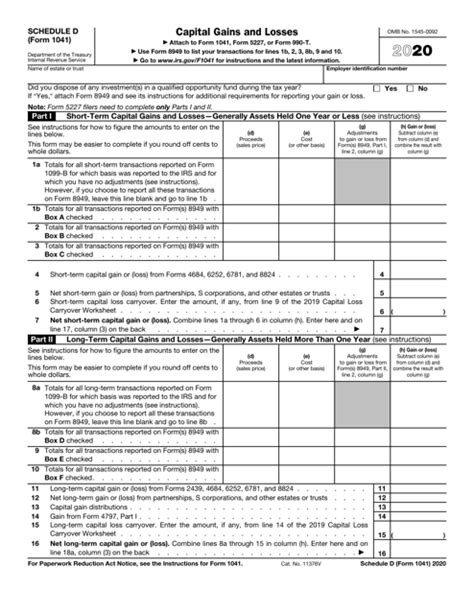
The Schedule D Form 1041 is a crucial document for fiduciaries and taxpayers who need to report capital gains and losses from the sale or exchange of assets. In this article, we will delve into the details of the Schedule D Form 1041, explaining its purpose, the types of capital gains and losses, and how to complete the form accurately.

Understanding the Schedule D Form 1041
The Schedule D Form 1041 is a supplemental form that is filed with the Form 1041, which is the income tax return for estates and trusts. The Schedule D Form 1041 is used to report the sale or exchange of capital assets, such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and other investment properties. The form is used to calculate the net gain or loss from these transactions and report it on the Form 1041.
Types of Capital Gains and Losses
There are two main types of capital gains and losses: short-term and long-term. Short-term capital gains and losses occur when an asset is sold or exchanged within one year of its acquisition. Long-term capital gains and losses occur when an asset is sold or exchanged after one year of its acquisition.
Short-Term Capital Gains and Losses
Short-term capital gains and losses are treated as ordinary income and are subject to the taxpayer's regular income tax rate. Short-term capital gains are reported on the Schedule D Form 1041 and are combined with other ordinary income on the Form 1041.
Long-Term Capital Gains and Losses
Long-term capital gains and losses are treated differently than short-term capital gains and losses. Long-term capital gains are subject to a lower tax rate, which is either 0%, 15%, or 20%, depending on the taxpayer's income tax bracket. Long-term capital losses can be used to offset long-term capital gains, and any excess losses can be carried forward to future years.

Completing the Schedule D Form 1041
To complete the Schedule D Form 1041, taxpayers will need to gather information about the sale or exchange of capital assets, including:
- The date of the sale or exchange
- The type of asset sold or exchanged
- The sale price or exchange value
- The cost basis of the asset
- Any commissions or fees paid
Taxpayers will also need to determine whether the gain or loss is short-term or long-term.
Step 1: List Each Asset Sold or Exchanged
On the Schedule D Form 1041, list each asset sold or exchanged during the tax year. Include the date of the sale or exchange, the type of asset, and the sale price or exchange value.
Step 2: Calculate the Gain or Loss
Calculate the gain or loss for each asset by subtracting the cost basis from the sale price or exchange value.
Step 3: Determine the Type of Gain or Loss
Determine whether the gain or loss is short-term or long-term based on the length of time the asset was held.
Step 4: Combine Gains and Losses
Combine the gains and losses from all assets sold or exchanged during the tax year.
Step 5: Calculate the Net Gain or Loss
Calculate the net gain or loss by combining the short-term and long-term gains and losses.

Example of Completing the Schedule D Form 1041
Let's say a taxpayer sold two assets during the tax year:
- Asset A: A stock that was held for six months and sold for $10,000. The cost basis was $8,000.
- Asset B: A piece of real estate that was held for three years and sold for $50,000. The cost basis was $40,000.
The taxpayer would list each asset on the Schedule D Form 1041, calculate the gain or loss, and determine the type of gain or loss.
| Asset | Date Sold | Sale Price | Cost Basis | Gain/Loss | Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asset A | 02/15/2022 | $10,000 | $8,000 | $2,000 | Short-term |
| Asset B | 08/20/2022 | $50,000 | $40,000 | $10,000 | Long-term |
The taxpayer would then combine the gains and losses and calculate the net gain or loss.
| Short-term | Long-term | Net Gain/Loss | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gain/Loss | $2,000 | $10,000 | $12,000 |
The taxpayer would report the net gain of $12,000 on the Form 1041.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When completing the Schedule D Form 1041, taxpayers should avoid common mistakes, such as:
- Failing to report all capital gains and losses
- Incorrectly determining the type of gain or loss
- Failing to calculate the correct net gain or loss
- Not carrying forward excess losses to future years

FAQs
Q: What is the purpose of the Schedule D Form 1041? A: The Schedule D Form 1041 is used to report capital gains and losses from the sale or exchange of assets.
Q: What is the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains and losses? A: Short-term capital gains and losses occur when an asset is sold or exchanged within one year of its acquisition, while long-term capital gains and losses occur when an asset is sold or exchanged after one year of its acquisition.
Q: How do I calculate the net gain or loss on the Schedule D Form 1041? A: To calculate the net gain or loss, combine the gains and losses from all assets sold or exchanged during the tax year, and then subtract any losses from gains.
What is the purpose of the Schedule D Form 1041?
+The Schedule D Form 1041 is used to report capital gains and losses from the sale or exchange of assets.
What is the difference between short-term and long-term capital gains and losses?
+Short-term capital gains and losses occur when an asset is sold or exchanged within one year of its acquisition, while long-term capital gains and losses occur when an asset is sold or exchanged after one year of its acquisition.
How do I calculate the net gain or loss on the Schedule D Form 1041?
+To calculate the net gain or loss, combine the gains and losses from all assets sold or exchanged during the tax year, and then subtract any losses from gains.
In conclusion, the Schedule D Form 1041 is an essential document for fiduciaries and taxpayers who need to report capital gains and losses from the sale or exchange of assets. By understanding the types of capital gains and losses, completing the form accurately, and avoiding common mistakes, taxpayers can ensure that they are in compliance with tax laws and regulations. If you have any questions or concerns about the Schedule D Form 1041, don't hesitate to reach out to a tax professional or comment below.