The fascinating world of biochemistry! Peptide bonds are the backbone of proteins, and understanding how they form is crucial for grasping the intricacies of life itself. In this article, we'll delve into the five primary ways peptide bonds form, shedding light on the intricate processes that govern protein synthesis.

What are Peptide Bonds?
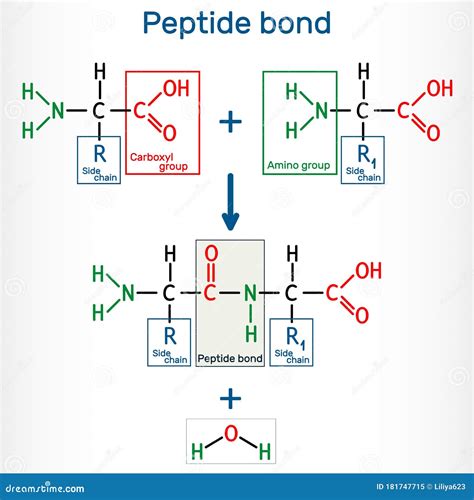
Before we dive into the ways peptide bonds form, let's quickly review what they are. A peptide bond is a type of covalent bond that forms between two amino acids, linking them together to create a polypeptide chain. This bond is characterized by the loss of a water molecule (dehydration) and the resulting formation of a peptide linkage between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another.
The Importance of Peptide Bonds
Peptide bonds are essential for the creation of proteins, which perform a wide range of functions in living organisms, from catalyzing metabolic reactions to replicating DNA. The unique properties of peptide bonds allow proteins to adopt specific three-dimensional structures, enabling them to interact with other molecules and carry out their biological functions.
1. Dehydration Synthesis
Dehydration synthesis is one of the most common methods of peptide bond formation. This process involves the reaction between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another, resulting in the loss of a water molecule and the formation of a peptide bond.

During dehydration synthesis, the amino group of one amino acid donates a proton (H+ ion) to the carboxyl group of another amino acid. This protonation enables the carboxyl group to lose a hydroxide ion (OH-), resulting in the formation of a peptide bond.
2. Enzyme-Catalyzed Synthesis
Enzyme-catalyzed synthesis is another way peptide bonds form. This process involves the use of enzymes, biological molecules that speed up chemical reactions, to facilitate the formation of peptide bonds.

During enzyme-catalyzed synthesis, the enzyme binds to the amino acids and positions them for optimal reaction. The enzyme then facilitates the transfer of a proton from the amino group to the carboxyl group, resulting in the formation of a peptide bond.
3. Chemical Synthesis
Chemical synthesis involves the use of chemical reagents to form peptide bonds. This method is often used in laboratory settings to synthesize peptides and proteins.

During chemical synthesis, the amino acids are treated with chemical reagents that facilitate the formation of peptide bonds. This process can be time-consuming and requires careful control of reaction conditions to avoid unwanted side reactions.
4. Solid-Phase Synthesis
Solid-phase synthesis is a technique used to synthesize peptides and proteins on a solid support, such as a resin.

During solid-phase synthesis, the amino acids are attached to the solid support and then activated for peptide bond formation. The process involves the sequential addition of amino acids to the growing peptide chain, with each step carefully controlled to ensure optimal reaction conditions.
5. Recombinant DNA Technology
Recombinant DNA technology involves the use of genetic engineering to produce peptides and proteins.

During recombinant DNA technology, the DNA sequence encoding the desired peptide or protein is inserted into a host organism, such as a bacterium or yeast. The host organism then expresses the peptide or protein, which can be purified and used for various applications.
Conclusion: Peptide Bond Formation in Perspective
In conclusion, peptide bond formation is a crucial process that underlies the creation of proteins, the building blocks of life. The five ways peptide bonds form – dehydration synthesis, enzyme-catalyzed synthesis, chemical synthesis, solid-phase synthesis, and recombinant DNA technology – each offer unique advantages and disadvantages. Understanding these processes is essential for appreciating the complexities of biochemistry and the importance of peptide bonds in living organisms.
What is the main function of peptide bonds?
+Peptide bonds are essential for the creation of proteins, which perform a wide range of functions in living organisms, from catalyzing metabolic reactions to replicating DNA.
What are the five primary ways peptide bonds form?
+The five primary ways peptide bonds form are dehydration synthesis, enzyme-catalyzed synthesis, chemical synthesis, solid-phase synthesis, and recombinant DNA technology.
What is the importance of understanding peptide bond formation?
+Understanding peptide bond formation is essential for appreciating the complexities of biochemistry and the importance of peptide bonds in living organisms.