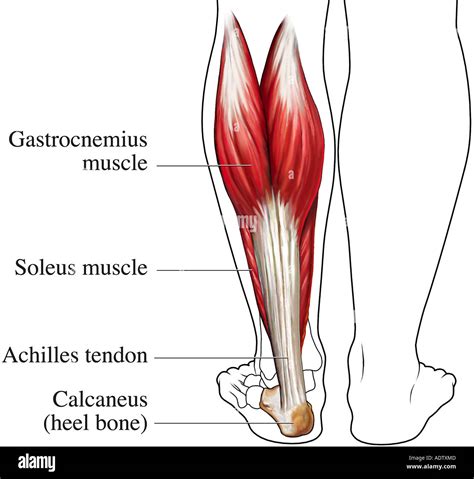
The Achilles tendon is one of the most vital tendons in the human body, playing a crucial role in facilitating movement and weight-bearing activities. Located at the back of the ankle, this tendon connects the calf muscles to the heel bone, enabling individuals to perform everyday tasks such as walking, running, and jumping. In this article, we will delve into the muscles forming the Achilles tendon, exploring their anatomy, functions, and importance in maintaining overall lower limb health.
The Achilles tendon is formed by the confluence of two muscles: the gastrocnemius and the soleus. These muscles work in conjunction to produce plantarflexion, the movement of pointing the foot downward.
Understanding the Gastrocnemius Muscle

The gastrocnemius muscle is a two-joint muscle, meaning it spans across two joints: the knee and the ankle. This muscle originates from the medial and lateral condyles of the femur (thigh bone) and inserts into the calcaneus (heel bone) via the Achilles tendon. The gastrocnemius muscle has two heads: the medial head and the lateral head, which merge to form a single tendon.
The primary function of the gastrocnemius muscle is to flex the foot downward and assist in knee flexion. This muscle is also responsible for decelerating the forward motion of the tibia (shin bone) during the swing phase of gait.
• Plantarflexion of the foot • Knee flexion • Deceleration of the tibia during the swing phase of gait
Understanding the Soleus Muscle

The soleus muscle is a one-joint muscle, spanning across the ankle joint. It originates from the posterior surface of the tibia and fibula (outer lower leg bone) and inserts into the calcaneus via the Achilles tendon. The soleus muscle is a slow-twitch muscle, meaning it is designed for endurance and postural control.
The primary function of the soleus muscle is to plantarflex the foot, controlling the movement of the ankle joint during weight-bearing activities.
• Plantarflexion of the foot • Postural control during weight-bearing activities • Assistance in decelerating the forward motion of the tibia during the swing phase of gait
The Achilles Tendon: A Crucial Structure

The Achilles tendon is the thickest and strongest tendon in the human body, with a thickness of approximately 1-2 cm. This tendon is formed by the merging of the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, transmitting forces from these muscles to the calcaneus.
The Achilles tendon plays a vital role in facilitating movement, enabling individuals to perform activities such as walking, running, and jumping. It also assists in maintaining posture and balance, particularly during single-leg stance activities.
• Transmission of forces from the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles to the calcaneus • Facilitation of movement, including walking, running, and jumping • Maintenance of posture and balance during weight-bearing activities
Importance of Maintaining Healthy Muscles and Tendons

Maintaining healthy muscles and tendons is crucial for overall lower limb health. Weak or imbalanced muscles can lead to tendon injuries, such as Achilles tendonitis or ruptures. Additionally, poor posture and biomechanics can put excessive stress on the Achilles tendon, leading to chronic pain and disability.
To maintain healthy muscles and tendons, it is essential to engage in regular exercise, incorporating activities that strengthen the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. Proper footwear, orthotics, and physical therapy can also help to alleviate excessive stress on the Achilles tendon.
• Engage in regular exercise, including strengthening activities for the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles • Wear proper footwear and orthotics to alleviate excessive stress on the Achilles tendon • Practice good posture and biomechanics to reduce stress on the Achilles tendon • Incorporate physical therapy to address muscle imbalances and tendon injuries
Conclusion
In conclusion, the muscles forming the Achilles tendon, specifically the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles, play a vital role in facilitating movement and maintaining overall lower limb health. Understanding the anatomy, functions, and importance of these muscles and tendons can help individuals prevent injuries and maintain optimal lower limb function. By engaging in regular exercise, practicing good posture and biomechanics, and addressing muscle imbalances and tendon injuries, individuals can maintain healthy muscles and tendons, enabling them to perform daily activities with confidence and ease.
We hope you found this article informative and helpful in understanding the muscles forming the Achilles tendon. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What are the two muscles that form the Achilles tendon?
+The two muscles that form the Achilles tendon are the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles.
What is the primary function of the gastrocnemius muscle?
+The primary function of the gastrocnemius muscle is to flex the foot downward and assist in knee flexion.
What is the importance of maintaining healthy muscles and tendons?
+Maintaining healthy muscles and tendons is crucial for overall lower limb health, preventing tendon injuries, and alleviating chronic pain and disability.