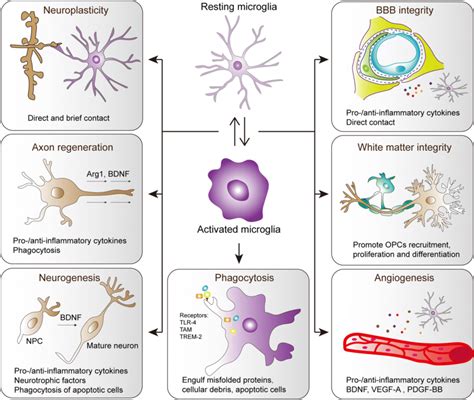
The human brain is a complex and intricate organ, and one of its most vital functions is to maintain the delicate balance between the brain and the rest of the body. One of the key components that help achieve this balance is the blood-brain barrier (BBB), a specialized barrier that regulates the flow of substances between the brain and the bloodstream. Recent research has shed light on the crucial role that microglial cells play in forming and maintaining the integrity of the BBB. In this article, we will explore the five ways microglial cells contribute to the formation of the BBB.

What are Microglial Cells?
Before we dive into the ways microglial cells form the BBB, it's essential to understand what microglial cells are. Microglial cells are a type of glial cell that acts as the primary immune cells of the central nervous system (CNS). They are responsible for monitoring the environment, removing pathogens and debris, and regulating the immune response. Microglial cells are highly dynamic and can change their shape and function in response to different stimuli.
Role of Microglial Cells in BBB Formation
Research has shown that microglial cells play a crucial role in the formation and maintenance of the BBB. Here are five ways microglial cells contribute to BBB formation:
- Production of Trophic Factors: Microglial cells produce trophic factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and fibroblast growth factor (FGF), which promote the growth and development of endothelial cells that form the BBB. These trophic factors also help to regulate the permeability of the BBB.
- Regulation of Endothelial Cell Junctions: Microglial cells release factors that regulate the formation and maintenance of tight junctions between endothelial cells. Tight junctions are essential for maintaining the integrity of the BBB and preventing the passage of substances from the bloodstream into the brain.
- Modulation of Immune Responses: Microglial cells regulate immune responses in the CNS by producing anti-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. This helps to prevent excessive inflammation, which can damage the BBB and compromise its integrity.
- Clearance of Debris and Pathogens: Microglial cells are responsible for removing debris and pathogens from the CNS, which helps to maintain the health and integrity of the BBB. By clearing away harmful substances, microglial cells help to prevent damage to the BBB and maintain its function.
- Regulation of Angiogenesis: Microglial cells regulate angiogenesis, the process of new blood vessel formation, in the CNS. By regulating angiogenesis, microglial cells help to ensure that the BBB is formed and maintained in a way that supports the health and function of the brain.
Consequences of Microglial Cell Dysfunction
Dysfunction of microglial cells has been implicated in various neurological and psychiatric disorders, including Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and depression. In these disorders, microglial cells may fail to regulate the immune response, clear debris and pathogens, or produce trophic factors, leading to BBB disruption and compromise. Understanding the role of microglial cells in BBB formation and maintenance is essential for developing new therapeutic strategies for these disorders.

Therapeutic Strategies for Microglial Cell Dysfunction
Several therapeutic strategies are being explored to target microglial cell dysfunction in neurological and psychiatric disorders. These include:
- Modulation of Microglial Cell Activation: Researchers are exploring ways to modulate microglial cell activation to prevent excessive inflammation and promote repair.
- Stimulation of Trophic Factor Production: Therapies that stimulate trophic factor production by microglial cells may help to promote BBB integrity and support brain health.
- Regulation of Angiogenesis: Targeting angiogenesis may help to promote BBB formation and maintenance in disorders characterized by microglial cell dysfunction.
Conclusion: A New Frontier in BBB Research
The discovery of the crucial role that microglial cells play in forming and maintaining the BBB has opened up a new frontier in BBB research. Further understanding of the mechanisms by which microglial cells regulate BBB formation and maintenance may lead to the development of new therapeutic strategies for neurological and psychiatric disorders. By exploring the complex interactions between microglial cells and the BBB, researchers may uncover new avenues for promoting brain health and preventing disease.

What is the blood-brain barrier?
+The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a specialized barrier that regulates the flow of substances between the brain and the bloodstream.
What is the role of microglial cells in the brain?
+Microglial cells are the primary immune cells of the central nervous system (CNS) and play a crucial role in monitoring the environment, removing pathogens and debris, and regulating the immune response.
How do microglial cells form the BBB?
+Microglial cells produce trophic factors, regulate endothelial cell junctions, modulate immune responses, clear debris and pathogens, and regulate angiogenesis to form and maintain the BBB.