Metal ions play a crucial role in various chemical reactions and biological processes. They are formed when metals lose or gain electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration. In this article, we will delve into the three types of ions formed by metals, their characteristics, and examples.
What are Metal Ions?

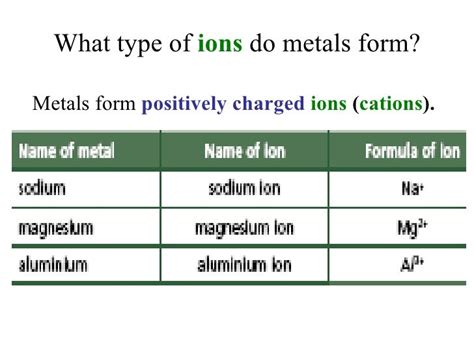
Metal ions are positively charged ions formed by the loss of one or more electrons from a metal atom. This process is known as ionization. Metal ions are also known as cations. They are typically formed by the loss of electrons from the outermost energy level of the metal atom.
Type 1: Monatomic Ions

Monatomic ions are ions formed by a single metal atom that has lost or gained electrons. They are the simplest type of ion and are typically formed by the alkali metals (Group 1) and alkaline earth metals (Group 2). Examples of monatomic ions include:
- Sodium ion (Na+)
- Calcium ion (Ca2+)
- Magnesium ion (Mg2+)
Monatomic ions are highly reactive and tend to form ionic bonds with other ions or molecules.
Characteristics of Monatomic Ions
- Formed by a single metal atom
- Typically formed by alkali metals and alkaline earth metals
- Highly reactive
- Tend to form ionic bonds
Type 2: Polyatomic Ions

Polyatomic ions are ions formed by a group of metal atoms that have lost or gained electrons. They are typically formed by transition metals (d-block elements) and post-transition metals (p-block elements). Examples of polyatomic ions include:
- Ammonium ion (NH4+)
- Copper(II) ion (Cu2+)
- Iron(III) ion (Fe3+)
Polyatomic ions are less reactive than monatomic ions and tend to form covalent bonds with other molecules.
Characteristics of Polyatomic Ions
- Formed by a group of metal atoms
- Typically formed by transition metals and post-transition metals
- Less reactive than monatomic ions
- Tend to form covalent bonds
Type 3: Complex Ions

Complex ions are ions formed by a central metal atom surrounded by one or more ligands (molecules or ions that donate electrons). They are typically formed by transition metals and are used in various biological and industrial applications. Examples of complex ions include:
- Tetraamminecopper(II) ion ([Cu(NH3)4]2+)
- Hexaaquairon(III) ion ([Fe(H2O)6]3+)
- Chloroplatinic acid ion ([PtCl6]2-)
Complex ions are highly stable and are used in various applications, including catalysis, medicine, and materials science.
Characteristics of Complex Ions
- Formed by a central metal atom surrounded by ligands
- Typically formed by transition metals
- Highly stable
- Used in various biological and industrial applications
In conclusion, metal ions play a crucial role in various chemical reactions and biological processes. Understanding the three types of ions formed by metals – monatomic, polyatomic, and complex ions – is essential for understanding their characteristics, properties, and applications.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of metal ions. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What are metal ions?
+Metal ions are positively charged ions formed by the loss of one or more electrons from a metal atom.
What are the three types of ions formed by metals?
+The three types of ions formed by metals are monatomic ions, polyatomic ions, and complex ions.
What are complex ions used for?
+Complex ions are used in various biological and industrial applications, including catalysis, medicine, and materials science.