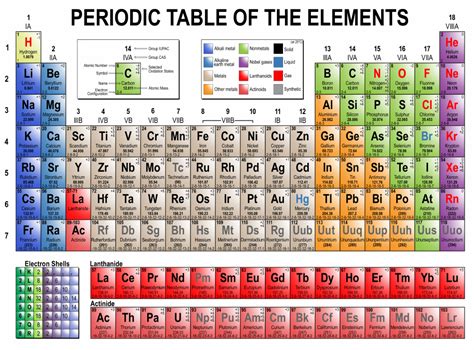
The periodic table of elements is a fundamental tool in chemistry, used to organize and classify the known chemical elements based on their atomic number, electron configuration, and recurring chemical properties. While the traditional periodic table is a familiar sight in classrooms and laboratories, there is a lesser-known variant that offers a more comprehensive and detailed view of the elements: the long form of the periodic table.

The long form of the periodic table, also known as the extended periodic table or the Janet table, is a tabular arrangement of the elements that extends the traditional periodic table to include all the known elements, including the synthetic and radioactive ones. This form of the periodic table was first proposed by Charles Janet in 1928 and has since been refined and updated to include new discoveries and advancements in chemistry.
The Benefits of the Long Form Periodic Table
So, why is the long form of the periodic table important? For starters, it provides a more complete and accurate representation of the elements, including those that are not typically included in the traditional periodic table. This is particularly useful for researchers and scientists who work with exotic or synthetic elements that are not well-represented in the traditional table.

Another benefit of the long form periodic table is that it offers a more detailed and nuanced view of the relationships between elements. By including all the known elements, the long form table reveals patterns and trends that are not apparent in the traditional table. This can be particularly useful for chemists and materials scientists who are looking to develop new materials or compounds with specific properties.
Understanding the Structure of the Long Form Periodic Table
So, what does the long form of the periodic table look like? The basic structure is similar to the traditional periodic table, with elements arranged in rows (periods) and columns (groups or families). However, the long form table extends the traditional table to include additional rows and columns that accommodate the synthetic and radioactive elements.

One of the key features of the long form periodic table is the inclusion of the actinide and lanthanide series, which are not typically included in the traditional table. These series include elements with atomic numbers ranging from 89 to 103 (actinides) and 57 to 71 (lanthanides), which are not well-represented in the traditional table.
How the Long Form Periodic Table is Used
So, how is the long form of the periodic table used in practice? One of the main applications is in the field of materials science, where researchers use the table to identify and develop new materials with specific properties. By examining the relationships between elements in the long form table, scientists can identify patterns and trends that can inform the development of new materials.

Another application of the long form periodic table is in the field of nuclear chemistry, where scientists use the table to understand the properties and behavior of radioactive elements. By examining the relationships between elements in the long form table, scientists can identify patterns and trends that can inform the development of new nuclear technologies.
The Challenges and Limitations of the Long Form Periodic Table
While the long form of the periodic table offers many benefits, it also presents some challenges and limitations. One of the main challenges is the sheer size and complexity of the table, which can make it difficult to navigate and interpret.

Another limitation of the long form periodic table is that it is not widely taught or used in educational settings. This can make it difficult for students and researchers to access and use the table, particularly if they are not familiar with its structure and organization.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the long form of the periodic table is a valuable tool for chemists, materials scientists, and nuclear chemists. By providing a more complete and accurate representation of the elements, the long form table offers a wealth of information and insights that can inform research and development in a wide range of fields.

We hope this article has inspired you to learn more about the long form of the periodic table and its many applications. Whether you are a researcher, student, or simply interested in chemistry, we invite you to share your thoughts and feedback in the comments below.
What is the long form of the periodic table?
+The long form of the periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the elements that extends the traditional periodic table to include all the known elements, including the synthetic and radioactive ones.
What are the benefits of the long form periodic table?
+The long form periodic table provides a more complete and accurate representation of the elements, including those that are not typically included in the traditional periodic table. It also offers a more detailed and nuanced view of the relationships between elements.
How is the long form periodic table used in practice?
+The long form periodic table is used in a variety of fields, including materials science and nuclear chemistry. Researchers use the table to identify and develop new materials with specific properties, and to understand the properties and behavior of radioactive elements.