Liposomes have been a subject of great interest in the scientific community for several decades. These microscopic vesicles have the ability to encapsulate a wide range of substances, from pharmaceuticals to nutrients, and deliver them to specific cells or tissues in the body. But have you ever wondered how liposomes are formed and why they are so important? In this article, we will delve into the five ways liposomes are formed and explore their significance in various fields.

What are Liposomes?
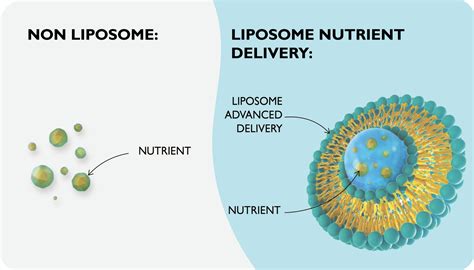
Before we dive into the formation of liposomes, let's briefly discuss what they are. Liposomes are tiny, spherical vesicles composed of a lipid bilayer, typically made up of phospholipids. They can range in size from 20 nanometers to several micrometers in diameter. The unique structure of liposomes allows them to encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances, making them ideal for a wide range of applications.
Methods of Liposome Formation
Liposomes can be formed using various methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Here are five common methods of liposome formation:
1. Thin-Film Hydration Method
The thin-film hydration method is one of the most common methods of liposome formation. This method involves dissolving lipids in an organic solvent, which is then evaporated to form a thin film. The film is then hydrated with an aqueous solution, causing the lipids to swell and form liposomes.

2. Sonication Method
The sonication method involves using high-frequency sound waves to disrupt the lipid bilayer and form liposomes. This method is commonly used to produce small, uniform liposomes.

3. Extrusion Method
The extrusion method involves forcing a lipid solution through a membrane with small pores, resulting in the formation of liposomes. This method is commonly used to produce large quantities of liposomes.

4. Reverse Phase Evaporation Method
The reverse phase evaporation method involves dissolving lipids in an organic solvent, which is then evaporated to form a gel-like substance. The gel is then hydrated with an aqueous solution, resulting in the formation of liposomes.

5. Microfluidization Method
The microfluidization method involves using a device to mix two streams of fluid, resulting in the formation of liposomes. This method is commonly used to produce small, uniform liposomes.

Importance of Liposomes
Liposomes have a wide range of applications, including:
Drug Delivery
Liposomes can be used to deliver pharmaceuticals directly to specific cells or tissues, reducing side effects and improving efficacy.
Nutrient Delivery
Liposomes can be used to deliver nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, directly to specific cells or tissues, improving absorption and utilization.
Gene Therapy
Liposomes can be used to deliver genetic material, such as DNA or RNA, to specific cells or tissues, allowing for the treatment of genetic diseases.
Cosmetics
Liposomes can be used in cosmetics to deliver active ingredients, such as antioxidants and anti-aging agents, directly to the skin.
Conclusion
In conclusion, liposomes are tiny, spherical vesicles that can be formed using various methods, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. The unique structure of liposomes allows them to encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic substances, making them ideal for a wide range of applications, including drug delivery, nutrient delivery, gene therapy, and cosmetics. We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of liposomes and their importance.
What are liposomes?
+Liposomes are tiny, spherical vesicles composed of a lipid bilayer, typically made up of phospholipids.
What are the methods of liposome formation?
+The five common methods of liposome formation are thin-film hydration, sonication, extrusion, reverse phase evaporation, and microfluidization.
What are the applications of liposomes?
+Liposomes have a wide range of applications, including drug delivery, nutrient delivery, gene therapy, and cosmetics.