Lipid bilayers are a crucial component of cell membranes, providing the basic framework that allows cells to function properly. The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is a thin layer of lipid and protein molecules that separates the cell from its environment. It is a semi-permeable membrane that regulates the movement of materials in and out of the cell, maintaining the cell's internal environment and facilitating communication with other cells.

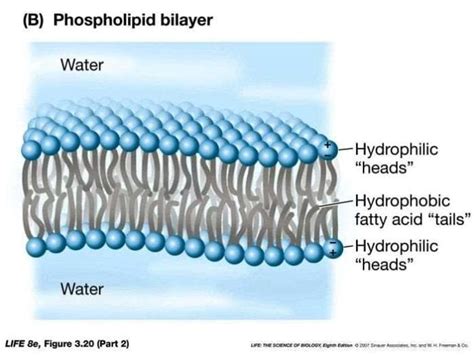
The lipid bilayer is composed of two layers of lipid molecules, with their hydrophilic (water-loving) heads facing outwards and their hydrophobic (water-fearing) tails facing inwards. This arrangement creates a stable and flexible structure that is essential for the proper functioning of the cell membrane. The lipid bilayer is semi-permeable, allowing certain molecules to pass through while keeping others out.
Structure of Lipid Bilayers
The structure of lipid bilayers is characterized by the arrangement of lipid molecules in a bilayer configuration. Each lipid molecule consists of a hydrophilic head group and a hydrophobic tail. The hydrophilic head group is composed of a phosphate group and a glycerol molecule, while the hydrophobic tail is composed of two fatty acid chains. The hydrophilic heads face outwards, interacting with the aqueous environment, while the hydrophobic tails face inwards, away from the water.

The lipid bilayer is stabilized by the interactions between the lipid molecules and the surrounding water molecules. The hydrophilic heads of the lipid molecules interact with the water molecules through hydrogen bonding, creating a stable and flexible structure. The hydrophobic tails of the lipid molecules interact with each other, creating a hydrophobic environment that is essential for the proper functioning of the cell membrane.
Components of Lipid Bilayers
Lipid bilayers are composed of several components, including:
- Phospholipids: These are the main components of lipid bilayers, accounting for approximately 50-70% of the total lipid content. Phospholipids consist of a hydrophilic head group and a hydrophobic tail.
- Cholesterol: This is a type of sterol that is present in lipid bilayers, accounting for approximately 10-20% of the total lipid content. Cholesterol helps to stabilize the lipid bilayer and maintain its fluidity.
- Glycolipids: These are lipid molecules that contain carbohydrate groups, accounting for approximately 5-10% of the total lipid content. Glycolipids play a role in cell-cell recognition and signaling.

Functions of Lipid Bilayers
Lipid bilayers play several crucial roles in the functioning of cells, including:
- Maintaining cell shape and structure: Lipid bilayers provide the structural framework that maintains the shape and structure of cells.
- Regulating the movement of materials: Lipid bilayers regulate the movement of materials in and out of cells, maintaining the cell's internal environment.
- Facilitating communication: Lipid bilayers facilitate communication between cells through the transmission of signals.
- Providing a platform for protein function: Lipid bilayers provide a platform for protein function, allowing proteins to interact with the cell membrane and perform their functions.

Importance of Lipid Bilayers in Biological Systems
Lipid bilayers are essential components of biological systems, playing a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and function of cells. Without lipid bilayers, cells would not be able to maintain their shape and structure, regulate the movement of materials, facilitate communication, or provide a platform for protein function.

In conclusion, lipid bilayers are a crucial component of cell membranes, providing the basic framework that allows cells to function properly. The structure and function of lipid bilayers are essential for maintaining the integrity and function of cells, and their importance cannot be overstated.
What are your thoughts on the importance of lipid bilayers in biological systems? Share your comments and let's continue the conversation!
What is the main component of lipid bilayers?
+Phospholipids are the main components of lipid bilayers, accounting for approximately 50-70% of the total lipid content.
What is the function of cholesterol in lipid bilayers?
+Cholesterol helps to stabilize the lipid bilayer and maintain its fluidity.
What is the importance of lipid bilayers in biological systems?
+Lipid bilayers are essential components of biological systems, playing a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and function of cells.