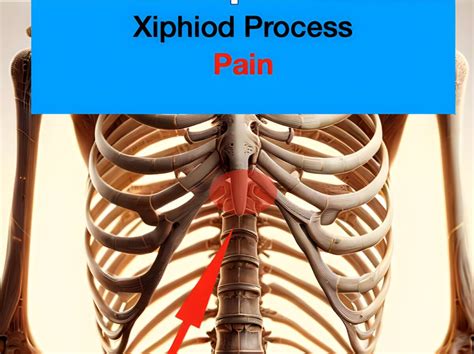
The xiphoid process, a small cartilaginous structure located at the lower end of the sternum, plays a crucial role in the anatomy of the human chest. While it may seem like a minor component, the xiphoid process is actually a vital landmark for various medical procedures, including artificial respiration. In this article, we will explore the five ways the xiphoid process relates to artificial respiration, highlighting its significance in this life-saving technique.
Understanding the Xiphoid Process

The xiphoid process is a small, cartilaginous structure that serves as the lowest point of the sternum. It is usually located at the level of the fifth intercostal space, near the junction of the ribcage and the abdomen. The xiphoid process is an important anatomical landmark, as it marks the boundary between the thoracic and abdominal cavities.
Importance of the Xiphoid Process in Anatomy
The xiphoid process is significant in anatomy because it provides a clear indication of the position of the heart and lungs within the thoracic cavity. It also serves as a reference point for various medical procedures, including artificial respiration. The xiphoid process is easily palpable, making it a useful landmark for healthcare professionals to locate the correct position for chest compressions and other life-saving interventions.
1. Landmark for Chest Compressions

One of the primary ways the xiphoid process relates to artificial respiration is as a landmark for chest compressions. During cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), the xiphoid process serves as a reference point for the correct placement of the hands for chest compressions. The American Heart Association recommends that the heel of the hand be placed on the center of the chest, just above the xiphoid process, to ensure effective chest compressions.
Technique for Chest Compressions
To perform chest compressions correctly, place the heel of one hand on the center of the chest, just above the xiphoid process. Place your other hand on top of the first hand, with your fingers interlaced. Push down on the chest with the heel of your hand to a depth of 2-3 inches, then release. Repeat this process at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute.
2. Reference Point for Ventilations

Another way the xiphoid process relates to artificial respiration is as a reference point for ventilations. During CPR, ventilations are performed by providing breaths to the patient through a bag-valve-mask device or an endotracheal tube. The xiphoid process serves as a landmark to ensure that the ventilation is being delivered to the correct location, just above the diaphragm.
Technique for Ventilations
To perform ventilations correctly, place the mask over the patient's nose and mouth, ensuring a tight seal. Squeeze the bag to deliver a breath, watching for the patient's chest to rise. The breath should be delivered at a rate of 12-20 breaths per minute, with a volume of 500-600 mL per breath.
3. Indicator of Chest Expansion

The xiphoid process also serves as an indicator of chest expansion during artificial respiration. As the patient receives ventilations, the xiphoid process should move upward, indicating that the lungs are expanding and the diaphragm is contracting. This movement is a good indicator of the effectiveness of the ventilations.
Monitoring Chest Expansion
To monitor chest expansion, place your hand on the patient's chest, with your fingers on either side of the xiphoid process. As the patient receives ventilations, watch for the xiphoid process to move upward, indicating that the lungs are expanding.
4. Guide for Intraosseous Access

In emergency situations, the xiphoid process may serve as a guide for intraosseous access. Intraosseous access involves inserting a needle into the bone marrow to administer medications or fluids. The xiphoid process provides a clear landmark for the correct placement of the needle, ensuring that the medication is delivered to the correct location.
Technique for Intraosseous Access
To perform intraosseous access, locate the xiphoid process and insert the needle at a 90-degree angle, just below the xiphoid process. Advance the needle to the correct depth, then administer the medication or fluid as needed.
5. Marker for Diaphragmatic Movement

Finally, the xiphoid process serves as a marker for diaphragmatic movement during artificial respiration. As the patient receives ventilations, the xiphoid process should move downward, indicating that the diaphragm is contracting and the lungs are expanding. This movement is a good indicator of the effectiveness of the ventilations.
Monitoring Diaphragmatic Movement
To monitor diaphragmatic movement, place your hand on the patient's abdomen, just below the xiphoid process. As the patient receives ventilations, watch for the xiphoid process to move downward, indicating that the diaphragm is contracting.
In conclusion, the xiphoid process plays a vital role in artificial respiration, serving as a landmark for chest compressions, ventilations, and intraosseous access. It also provides a clear indicator of chest expansion and diaphragmatic movement. By understanding the significance of the xiphoid process in artificial respiration, healthcare professionals can provide more effective life-saving interventions.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences with artificial respiration and the xiphoid process in the comments below. Have you ever had to perform CPR or provide ventilations in an emergency situation? How did you use the xiphoid process as a landmark? Share your stories and help us create a community of healthcare professionals dedicated to providing the best possible care.
What is the xiphoid process and where is it located?
+The xiphoid process is a small cartilaginous structure located at the lower end of the sternum, usually at the level of the fifth intercostal space.
Why is the xiphoid process important in artificial respiration?
+The xiphoid process serves as a landmark for chest compressions, ventilations, and intraosseous access, and provides a clear indicator of chest expansion and diaphragmatic movement.
How do I locate the xiphoid process during CPR?
+Locate the xiphoid process by feeling for the lowest point of the sternum, usually at the level of the fifth intercostal space.