Iron is one of the most abundant elements on Earth and plays a crucial role in various biological, chemical, and physical processes. Understanding the electron configuration of iron is essential to grasp its chemical properties, reactivity, and behavior in different environments. In this article, we will delve into the world of iron electron configuration, exploring its significance, notation, and implications.
What is Electron Configuration?

Electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons in an atom, which is a crucial factor in determining its chemical properties. The configuration is typically represented using the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle. The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels, while the Pauli exclusion principle states that each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons with opposite spins.
Iron Electron Configuration Notation
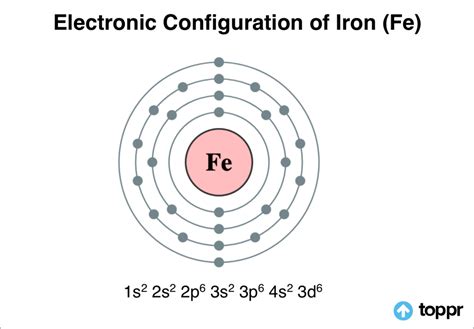
The electron configuration of iron is typically represented as [Ar] 3d6 4s2. This notation indicates that the iron atom has:
- A noble gas core (argon) with a full outer energy level
- Six electrons in the 3d orbital
- Two electrons in the 4s orbital
This notation provides a concise way to describe the arrangement of electrons in an iron atom.
Understanding the Iron Electron Configuration
To fully grasp the iron electron configuration, it's essential to understand the different energy levels and orbitals involved. The iron atom has 26 electrons, which are distributed across various energy levels.
- The 1s, 2s, and 2p orbitals are fully occupied, with two electrons in each orbital.
- The 3s and 3p orbitals are also fully occupied, with two electrons in each orbital.
- The 3d orbital has six electrons, which is less than the maximum capacity of ten electrons.
- The 4s orbital has two electrons.
The partially filled 3d orbital is responsible for the unique chemical properties of iron, including its ability to form ions and compounds with various oxidation states.
Importance of Iron Electron Configuration

The iron electron configuration plays a vital role in various biological, chemical, and physical processes. Some of the key implications include:
- Biological significance: Iron is essential for the transport of oxygen in the blood, and its electron configuration allows it to bind to oxygen molecules.
- Chemical reactivity: The partially filled 3d orbital makes iron highly reactive, allowing it to form ions and compounds with various oxidation states.
- Magnetic properties: The unpaired electrons in the 3d orbital contribute to the magnetic properties of iron, making it ferromagnetic.
Electron Configuration of Iron Ions
When iron forms ions, its electron configuration changes. The most common ions of iron are Fe2+ and Fe3+.
- Fe2+ ion: The electron configuration of the Fe2+ ion is [Ar] 3d6. The removal of two electrons from the 4s orbital results in a partially filled 3d orbital.
- Fe3+ ion: The electron configuration of the Fe3+ ion is [Ar] 3d5. The removal of three electrons from the 4s and 3d orbitals results in a partially filled 3d orbital.
Understanding the electron configuration of iron ions is crucial for predicting their chemical behavior and reactivity.
Electron Configuration and the Periodic Table

The electron configuration of iron is closely related to its position in the periodic table. Iron is a transition metal, which means it is located in the d-block of the periodic table.
- Transition metals: The transition metals are characterized by partially filled d orbitals, which are responsible for their unique chemical properties.
- Periodic trends: The electron configuration of iron follows the periodic trends of the transition metals, with the 3d orbital being partially filled.
Conclusion and Future Directions
In conclusion, the iron electron configuration is a fundamental concept in understanding the chemical properties and behavior of iron. The partially filled 3d orbital makes iron highly reactive and essential for various biological, chemical, and physical processes.
Future research directions include:
- Advanced materials: Understanding the electron configuration of iron is crucial for the development of advanced materials, such as iron-based alloys and catalysts.
- Biological applications: The iron electron configuration has significant implications for biological applications, including the development of iron-based drugs and diagnostic tools.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive understanding of the iron electron configuration and its significance in various fields. Share your thoughts and comments below!
What is the electron configuration of iron?
+The electron configuration of iron is [Ar] 3d6 4s2.
Why is the iron electron configuration important?
+The iron electron configuration is essential for understanding its chemical properties, reactivity, and behavior in different environments.
What are the implications of the iron electron configuration?
+The iron electron configuration has significant implications for biological, chemical, and physical processes, including the transport of oxygen in the blood, magnetic properties, and chemical reactivity.