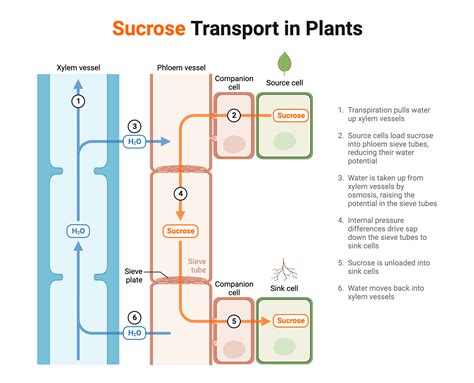
Plants are the primary producers of the Earth's ecosystem, and their ability to transport glucose and other sugars is crucial for their growth, development, and reproduction. Glucose transport in plants is a complex process that involves the coordinated effort of multiple cell types, tissues, and organs. One of the key players in this process is sucrose, a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose molecules. In this article, we will delve into the role of sucrose in glucose transport in plants and explore the mechanisms, benefits, and importance of this process.

What is Sucrose and its Role in Plant Metabolism?
Sucrose is a naturally occurring disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose molecules. It is the primary form of sugar transported in plants and serves as a key energy source for growth and development. Sucrose is synthesized in the leaves of plants through photosynthesis, where carbon dioxide and water are converted into glucose and oxygen. The glucose molecules are then combined with fructose molecules to form sucrose, which is transported to other parts of the plant through the phloem tissue.
Sucrose plays a critical role in plant metabolism, serving as a source of energy, carbon skeletons, and reducing power for various metabolic processes. It is also involved in the regulation of gene expression, hormone signaling, and stress responses. In addition, sucrose is a key component of plant defense mechanisms, serving as a signaling molecule that triggers the production of defense-related genes.
Glucose Transport in Plants: The Phloem Tissue
The phloem tissue is responsible for the long-distance transport of sucrose and other sugars in plants. It is a complex network of cells that forms a continuum from the leaves to the roots, allowing for the bidirectional transport of sugars, amino acids, and other nutrients. The phloem tissue is composed of several cell types, including sieve elements, companion cells, and phloem parenchyma cells.
Sieve elements are the primary cells responsible for sugar transport in the phloem tissue. They are long, thin cells that form a tube-like structure, allowing for the rapid transport of sugars over long distances. Companion cells are smaller cells that surround the sieve elements and play a crucial role in loading and unloading sugars into and out of the sieve elements. Phloem parenchyma cells are responsible for the synthesis and storage of sucrose and other sugars.
Mechanisms of Glucose Transport in Plants
Glucose transport in plants involves several mechanisms, including:
- Symplastic transport: This involves the movement of sugars through the cytoplasm of adjacent cells, connected by plasmodesmata.
- Apoplastic transport: This involves the movement of sugars through the cell wall and intercellular spaces, requiring the use of transport proteins.
- Phloem loading: This involves the uptake of sugars into the phloem tissue, mediated by transport proteins.
- Phloem unloading: This involves the release of sugars from the phloem tissue, mediated by transport proteins.
These mechanisms work together to ensure the efficient transport of sucrose and other sugars throughout the plant, allowing for the distribution of energy and nutrients to various tissues and organs.
Benefits of Glucose Transport in Plants
Glucose transport in plants has several benefits, including:
- Energy supply: Sucrose serves as a primary source of energy for plant growth and development.
- Carbon skeletons: Sucrose provides carbon skeletons for the synthesis of amino acids, fatty acids, and other biomolecules.
- Reducing power: Sucrose is involved in the regulation of reducing power, allowing for the reduction of oxidized molecules.
- Defense mechanisms: Sucrose is involved in the regulation of defense-related genes, providing protection against pathogens and pests.
Importance of Sucrose in Glucose Transport
Sucrose is the primary form of sugar transported in plants, and its importance cannot be overstated. Sucrose:
- Regulates gene expression: Sucrose is involved in the regulation of gene expression, influencing the production of proteins and other biomolecules.
- Influences hormone signaling: Sucrose is involved in hormone signaling pathways, regulating plant growth and development.
- Provides reducing power: Sucrose is involved in the regulation of reducing power, allowing for the reduction of oxidized molecules.

Factors Affecting Glucose Transport in Plants
Several factors can affect glucose transport in plants, including:
- Temperature: Temperature affects the rate of photosynthesis and sucrose synthesis.
- Light intensity: Light intensity affects the rate of photosynthesis and sucrose synthesis.
- Water availability: Water availability affects the rate of photosynthesis and sucrose synthesis.
- Nutrient availability: Nutrient availability affects the rate of sucrose synthesis and transport.
Practical Applications of Glucose Transport in Plants
Understanding glucose transport in plants has several practical applications, including:
- Crop improvement: Understanding glucose transport can lead to the development of crops with improved yields and stress tolerance.
- Plant breeding: Understanding glucose transport can lead to the development of crops with improved sugar content and quality.
- Biotechnology: Understanding glucose transport can lead to the development of biotechnological applications, such as the production of biofuels and bioproducts.

Conclusion
Glucose transport in plants is a complex process that involves the coordinated effort of multiple cell types, tissues, and organs. Sucrose plays a critical role in this process, serving as a primary source of energy, carbon skeletons, and reducing power. Understanding glucose transport in plants has several practical applications, including crop improvement, plant breeding, and biotechnology. Further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms of glucose transport in plants and to develop new technologies that can improve crop yields and stress tolerance.
Get Involved!
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of glucose transport in plants. Share your thoughts and comments below! Do you have any questions or topics you'd like to discuss further? Join the conversation and let's explore the world of plant biology together!
FAQ Section
What is sucrose and its role in plant metabolism?
+Sucrose is a disaccharide composed of glucose and fructose molecules. It is the primary form of sugar transported in plants and serves as a source of energy, carbon skeletons, and reducing power for various metabolic processes.
What is the phloem tissue and its role in glucose transport?
+The phloem tissue is a complex network of cells that forms a continuum from the leaves to the roots, allowing for the bidirectional transport of sugars, amino acids, and other nutrients. It is responsible for the long-distance transport of sucrose and other sugars in plants.
What are the mechanisms of glucose transport in plants?
+Glucose transport in plants involves several mechanisms, including symplastic transport, apoplastic transport, phloem loading, and phloem unloading. These mechanisms work together to ensure the efficient transport of sucrose and other sugars throughout the plant.