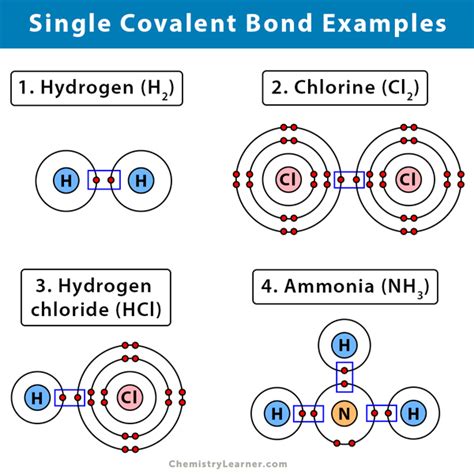
Carbon is a unique element in the periodic table, known for its ability to form a wide variety of compounds. One of the key reasons for this versatility is its ability to form single covalent bonds with other atoms. In this article, we will explore the concept of single covalent bonding in carbon and its limitations.
Carbon's Ability to Form Single Covalent Bonds
Carbon has four valence electrons, which are the electrons in its outermost energy level. These electrons are available for bonding with other atoms. Carbon's atomic structure allows it to form four single covalent bonds with other atoms, which is known as tetravalency. This means that carbon can bond with four other atoms, either of the same element or different elements.
The ability of carbon to form single covalent bonds is due to its relatively small atomic size and moderate electronegativity. Electronegativity is the measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons towards itself. Carbon has an electronegativity of 2.5, which is moderate compared to other elements. This allows carbon to form stable bonds with other atoms.

Limitations of Carbon's Single Covalent Bonding
While carbon's ability to form single covalent bonds is a key factor in its versatility, there are some limitations to this ability. One of the main limitations is the maximum number of bonds that carbon can form.
As mentioned earlier, carbon can form four single covalent bonds with other atoms. This is because carbon has four valence electrons, which are available for bonding. If carbon were to form more than four bonds, it would require additional electrons, which is not possible.
Another limitation of carbon's single covalent bonding is the type of atoms it can bond with. Carbon can only form stable bonds with atoms that have a moderate electronegativity, such as hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. If carbon were to bond with atoms that have a high electronegativity, such as fluorine, the bond would be unstable.
Carbon's Four Single Covalent Bonds
Carbon's four single covalent bonds are the key to its versatility in forming a wide variety of compounds. These bonds are typically represented by the symbol "C" in chemical formulas. The four bonds are:
- C-H (carbon-hydrogen bond)
- C-O (carbon-oxygen bond)
- C-N (carbon-nitrogen bond)
- C-C (carbon-carbon bond)
Each of these bonds has a specific bond length and bond energy, which are important factors in determining the properties of the compound.

Carbon-Hydrogen Bond
The carbon-hydrogen bond is one of the most common bonds in organic compounds. It is a relatively weak bond, with a bond energy of around 410 kJ/mol. This bond is typically represented by the symbol "C-H" in chemical formulas.
Carbon-Oxygen Bond
The carbon-oxygen bond is another common bond in organic compounds. It is a relatively strong bond, with a bond energy of around 750 kJ/mol. This bond is typically represented by the symbol "C-O" in chemical formulas.

Carbon-Nitrogen Bond
The carbon-nitrogen bond is a relatively strong bond, with a bond energy of around 870 kJ/mol. This bond is typically represented by the symbol "C-N" in chemical formulas.
Carbon-Carbon Bond
The carbon-carbon bond is a relatively strong bond, with a bond energy of around 620 kJ/mol. This bond is typically represented by the symbol "C-C" in chemical formulas.

Conclusion
In conclusion, carbon's ability to form single covalent bonds is a key factor in its versatility in forming a wide variety of compounds. However, there are some limitations to this ability, including the maximum number of bonds that carbon can form and the type of atoms it can bond with. Understanding these limitations is important in predicting the properties and behavior of carbon-based compounds.
We invite you to share your thoughts on this topic and ask any questions you may have in the comments section below. Additionally, if you found this article informative, please share it with others who may benefit from it.
What is the maximum number of bonds that carbon can form?
+Carbon can form a maximum of four single covalent bonds with other atoms.
What type of atoms can carbon bond with?
+Carbon can only form stable bonds with atoms that have a moderate electronegativity, such as hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen.
What is the bond energy of the carbon-hydrogen bond?
+The bond energy of the carbon-hydrogen bond is around 410 kJ/mol.