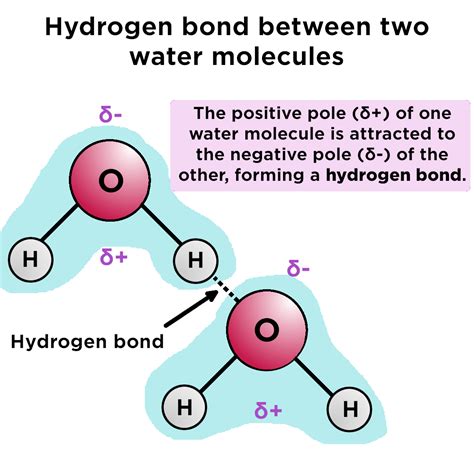
Water is the most abundant substance on Earth, and its unique properties make it essential for life as we know it. One of the most fascinating aspects of water is its ability to form hydrogen bonds, which play a crucial role in its structure, properties, and biological functions. In this article, we will delve into the world of water molecules, exploring the concept of hydrogen bonds, their capacity, and the impact on water's behavior.
What are Hydrogen Bonds?

Hydrogen bonds are a type of intermolecular force that arises between molecules with a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine. In the case of water, the hydrogen atoms are bonded to oxygen, which is highly electronegative. This creates a partial positive charge on the hydrogen atoms and a partial negative charge on the oxygen atom.
When two water molecules are in close proximity, the partial positive charge on the hydrogen atom of one molecule is attracted to the partial negative charge on the oxygen atom of another molecule. This attraction is known as a hydrogen bond. Hydrogen bonds are relatively weak compared to covalent bonds, but they play a vital role in the structure and properties of water.
Hydrogen Bond Capacity of Water Molecules

The hydrogen bond capacity of water molecules refers to the number of hydrogen bonds that a single water molecule can form with its neighboring molecules. In the case of water, each molecule can form up to four hydrogen bonds: two as a donor and two as an acceptor.
The donor-acceptor mechanism of hydrogen bonding in water is as follows:
- A water molecule can donate two hydrogen atoms to form hydrogen bonds with neighboring molecules.
- A water molecule can accept two hydrogen atoms from neighboring molecules to form hydrogen bonds.
This tetrahedral arrangement of hydrogen bonds around a water molecule is known as the "hydrogen bond network." The hydrogen bond network is responsible for many of the unique properties of water, including its high surface tension, boiling point, and ability to dissolve a wide range of substances.
Impact of Hydrogen Bonds on Water's Behavior

The hydrogen bond network in water has a significant impact on its behavior and properties. Some of the key effects of hydrogen bonds on water's behavior include:
- High surface tension: The hydrogen bond network creates a "skin" on the surface of water, which gives it a high surface tension. This is why water can resist external forces, such as gravity, and maintain its shape against gravity.
- High boiling point: The hydrogen bond network requires a significant amount of energy to break, which is why water has a relatively high boiling point compared to other substances.
- High specific heat capacity: The hydrogen bond network also allows water to absorb and release heat energy slowly, which is why it has a high specific heat capacity.
- Solubility: The hydrogen bond network enables water to dissolve a wide range of substances, including salts, sugars, and other polar molecules.
Biological Importance of Hydrogen Bonds in Water

Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the biological functions of water. Some of the key biological importance of hydrogen bonds in water include:
- Protein structure and function: Hydrogen bonds are essential for the structure and function of proteins, which are the building blocks of life.
- Cell membrane structure: Hydrogen bonds help to maintain the structure and function of cell membranes, which are the barriers that separate the cell from its environment.
- DNA and RNA structure: Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the structure and function of DNA and RNA, which are the genetic materials of life.
Practical Applications of Hydrogen Bonds in Water

The hydrogen bond network in water has many practical applications in various fields, including:
- Water treatment: Understanding the hydrogen bond network in water is essential for developing effective water treatment technologies.
- Biotechnology: Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the development of biotechnology products, such as protein-based therapeutics.
- Food industry: Hydrogen bonds are essential for the texture and stability of many food products, such as ice cream and mayonnaise.
What is the hydrogen bond capacity of a water molecule?
+A water molecule can form up to four hydrogen bonds: two as a donor and two as an acceptor.
What is the impact of hydrogen bonds on water's behavior?
+The hydrogen bond network in water has a significant impact on its behavior and properties, including its high surface tension, boiling point, and ability to dissolve a wide range of substances.
What is the biological importance of hydrogen bonds in water?
+Hydrogen bonds play a crucial role in the biological functions of water, including protein structure and function, cell membrane structure, and DNA and RNA structure.
We hope you found this article informative and engaging. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.