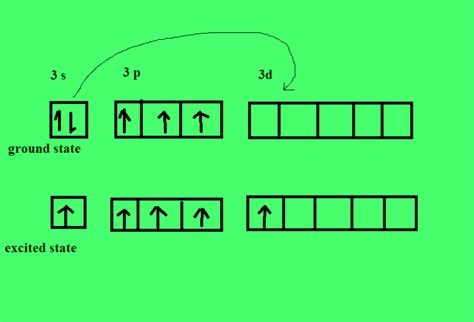
Phosphorus is a versatile element that can form a wide variety of bonds with other elements, resulting in a vast array of compounds with diverse properties and applications. In this article, we will explore five types of bonds that phosphorus can form, highlighting their characteristics, examples, and significance.
Phosphorus is a highly reactive element, and its ability to form bonds with other elements is due to its unique electronic configuration. Phosphorus has five valence electrons, which it can share with other elements to form covalent bonds. Additionally, phosphorus can also form ionic bonds, coordinate covalent bonds, and hydrogen bonds, making it a highly versatile element in terms of bonding.
Phosphorus-Oxygen Bonds

Phosphorus-oxygen bonds are one of the most common types of bonds formed by phosphorus. These bonds are typically covalent and are found in a wide range of compounds, including phosphates, phosphites, and phosphonates. Phosphorus-oxygen bonds are strong and stable, making them an essential component of many biological molecules, such as DNA and ATP.
Examples of phosphorus-oxygen bonds include:
- Phosphate esters, which are used as building blocks for DNA and RNA
- Phospholipids, which are essential components of cell membranes
- ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the energy currency of the cell
Properties of Phosphorus-Oxygen Bonds
- Strong and stable
- Covalent
- Found in a wide range of biological molecules
- Essential for energy transfer and storage
Phosphorus-Carbon Bonds

Phosphorus-carbon bonds are another important type of bond formed by phosphorus. These bonds are typically covalent and are found in a wide range of organic compounds, including phosphines, phosphonium salts, and ylides. Phosphorus-carbon bonds are strong and stable, making them an essential component of many pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals.
Examples of phosphorus-carbon bonds include:
- Phosphines, which are used as ligands in homogeneous catalysis
- Phosphonium salts, which are used as phase-transfer catalysts
- Ylides, which are used as reagents in organic synthesis
Properties of Phosphorus-Carbon Bonds
- Strong and stable
- Covalent
- Found in a wide range of organic compounds
- Essential for catalysis and organic synthesis
Phosphorus-Nitrogen Bonds

Phosphorus-nitrogen bonds are a type of bond formed by phosphorus that is typically covalent. These bonds are found in a wide range of compounds, including phosphazenes, phosphinimines, and phosphorus-containing heterocycles. Phosphorus-nitrogen bonds are strong and stable, making them an essential component of many materials with unique properties.
Examples of phosphorus-nitrogen bonds include:
- Phosphazenes, which are used as precursors to high-performance materials
- Phosphinimines, which are used as reagents in organic synthesis
- Phosphorus-containing heterocycles, which are used as pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals
Properties of Phosphorus-Nitrogen Bonds
- Strong and stable
- Covalent
- Found in a wide range of compounds
- Essential for materials science and organic synthesis
Phosphorus-Sulfur Bonds

Phosphorus-sulfur bonds are a type of bond formed by phosphorus that is typically covalent. These bonds are found in a wide range of compounds, including phosphorothioates, phosphorodithioates, and thiophosphates. Phosphorus-sulfur bonds are strong and stable, making them an essential component of many agricultural chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
Examples of phosphorus-sulfur bonds include:
- Phosphorothioates, which are used as insecticides and herbicides
- Phosphorodithioates, which are used as pesticides and fungicides
- Thiophosphates, which are used as precursors to high-performance materials
Properties of Phosphorus-Sulfur Bonds
- Strong and stable
- Covalent
- Found in a wide range of compounds
- Essential for agriculture and pharmaceuticals
Phosphorus-Metal Bonds

Phosphorus-metal bonds are a type of bond formed by phosphorus that is typically ionic or coordinate covalent. These bonds are found in a wide range of compounds, including phosphine complexes, phosphite complexes, and phosphorus-containing metal-organic frameworks. Phosphorus-metal bonds are strong and stable, making them an essential component of many catalysts and materials with unique properties.
Examples of phosphorus-metal bonds include:
- Phosphine complexes, which are used as ligands in homogeneous catalysis
- Phosphite complexes, which are used as catalysts in organic synthesis
- Phosphorus-containing metal-organic frameworks, which are used as materials for gas storage and separation
Properties of Phosphorus-Metal Bonds
- Strong and stable
- Ionic or coordinate covalent
- Found in a wide range of compounds
- Essential for catalysis and materials science
In conclusion, phosphorus is a highly versatile element that can form a wide variety of bonds with other elements, resulting in a vast array of compounds with diverse properties and applications. The five types of bonds formed by phosphorus that we have discussed in this article - phosphorus-oxygen bonds, phosphorus-carbon bonds, phosphorus-nitrogen bonds, phosphorus-sulfur bonds, and phosphorus-metal bonds - are essential components of many biological molecules, materials, and catalysts.
We hope that this article has provided you with a comprehensive overview of the different types of bonds that phosphorus can form. We encourage you to share this article with others and to continue learning about the fascinating world of chemistry!
What are the five types of bonds that phosphorus can form?
+Phosphorus can form phosphorus-oxygen bonds, phosphorus-carbon bonds, phosphorus-nitrogen bonds, phosphorus-sulfur bonds, and phosphorus-metal bonds.
What are phosphorus-oxygen bonds used for?
+Phosphorus-oxygen bonds are used in a wide range of biological molecules, including DNA and ATP.
What are phosphorus-carbon bonds used for?
+Phosphorus-carbon bonds are used in a wide range of organic compounds, including phosphines, phosphonium salts, and ylides.