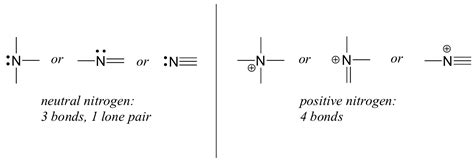
Nitrogen is a fascinating element that plays a crucial role in many biological and chemical processes. One of the most interesting aspects of nitrogen is its ability to form bonds with other atoms. But have you ever wondered how many bonds nitrogen can form at once?
Nitrogen's unique electronic configuration allows it to form multiple bonds with other atoms, making it a versatile element in many chemical reactions. In this article, we'll delve into the world of nitrogen bonding and explore the maximum number of bonds nitrogen can form simultaneously.
Understanding Nitrogen's Electronic Configuration
To comprehend how many bonds nitrogen can form, we need to understand its electronic configuration. Nitrogen has an atomic number of 7, which means it has 7 electrons in its atomic orbitals. The electronic configuration of nitrogen is 1s² 2s² 2p³, indicating that it has 5 valence electrons.
Valence Electrons and Bonding Capacity
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost energy level of an atom, which participate in chemical bonding. Nitrogen's 5 valence electrons make it capable of forming multiple bonds with other atoms. The number of bonds an atom can form is determined by the number of unpaired electrons in its valence shell.
Nitrogen's Bonding Capacity
Nitrogen can form a maximum of 4 bonds at once. This is because nitrogen has 5 valence electrons, and when it forms bonds, it shares one pair of electrons with each bonded atom. This leaves one unpaired electron, which can participate in forming an additional bond.
Types of Nitrogen Bonds
Nitrogen can form several types of bonds, including:
- Single bonds: Nitrogen can form single bonds with other atoms by sharing one pair of electrons. Examples include ammonia (NH₃) and nitrogen gas (N₂).
- Double bonds: Nitrogen can form double bonds with other atoms by sharing two pairs of electrons. Examples include nitrogen dioxide (NO₂) and nitric acid (HNO₃).
- Triple bonds: Nitrogen can form triple bonds with other atoms by sharing three pairs of electrons. Examples include nitrogen gas (N₂) and cyanide (CN⁻).
Examples of Nitrogen's Bonding Capacity
Let's consider some examples of nitrogen's bonding capacity:
- Ammonia (NH₃): In ammonia, nitrogen forms three single bonds with hydrogen atoms, using three of its valence electrons. The remaining two electrons are unpaired and can participate in forming an additional bond.
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO₂): In nitrogen dioxide, nitrogen forms a double bond with oxygen, using two of its valence electrons. The remaining three electrons are unpaired and can participate in forming additional bonds.
- Cyanide (CN⁻): In cyanide, nitrogen forms a triple bond with carbon, using three of its valence electrons. The remaining two electrons are unpaired and can participate in forming an additional bond.
Practical Applications of Nitrogen's Bonding Capacity
Nitrogen's ability to form multiple bonds has numerous practical applications in various fields, including:
- Agriculture: Nitrogen-based fertilizers, such as ammonia and nitric acid, are essential for plant growth and crop production.
- Pharmaceuticals: Nitrogen-containing compounds, such as amino acids and nucleotides, are crucial for the development of medicines and therapies.
- Materials Science: Nitrogen-based materials, such as silicon nitride and aluminum nitride, have unique properties that make them useful in various industrial applications.

Conclusion
In conclusion, nitrogen's unique electronic configuration allows it to form multiple bonds with other atoms, making it a versatile element in many chemical reactions. Nitrogen can form a maximum of 4 bonds at once, which is essential for its role in various biological and chemical processes. Understanding nitrogen's bonding capacity is crucial for appreciating its importance in various fields, from agriculture to pharmaceuticals.
Share Your Thoughts
We hope this article has helped you understand nitrogen's bonding capacity. Share your thoughts and comments below! How do you think nitrogen's bonding capacity affects its role in various chemical reactions?
FAQ Section
What is the electronic configuration of nitrogen?
+Nitrogen's electronic configuration is 1s² 2s² 2p³.
How many bonds can nitrogen form at once?
+Nitrogen can form a maximum of 4 bonds at once.
What are some examples of nitrogen's bonding capacity?
+Examples of nitrogen's bonding capacity include ammonia (NH₃), nitrogen dioxide (NO₂), and cyanide (CN⁻).