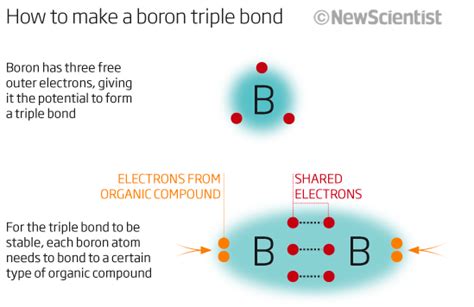
Boron, the fifth element on the periodic table, is a unique and versatile element that can form a variety of bonds with other elements. Its small size, high ionization energy, and ability to form three-center bonds make it an interesting subject of study in chemistry. In this article, we will explore three types of bonds that boron can form.

h2>Single Bonds (σ Bonds)
Boron can form single bonds with other elements, such as hydrogen, carbon, and nitrogen. These bonds are formed when a boron atom shares one pair of electrons with another atom. Single bonds are typically strong and stable, but they can be broken by external energy sources.
One example of a single bond formed by boron is in the compound borane (BH3). In this molecule, the boron atom forms three single bonds with hydrogen atoms, resulting in a trigonal planar geometry.
h3>Types of Single Bonds
Boron can form different types of single bonds, including:
- σ bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals along the bond axis.
- π bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals perpendicular to the bond axis.
h2>Double Bonds (σ and π Bonds)
Boron can also form double bonds with other elements, such as oxygen and sulfur. Double bonds are formed when a boron atom shares two pairs of electrons with another atom. Double bonds are typically stronger than single bonds and are more resistant to external energy sources.
One example of a double bond formed by boron is in the compound boron oxide (B2O3). In this molecule, the boron atoms form double bonds with oxygen atoms, resulting in a planar geometry.

h3>Types of Double Bonds
Boron can form different types of double bonds, including:
- σ-π bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals along the bond axis and perpendicular to the bond axis.
- π-π bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals perpendicular to the bond axis.
h2>Three-Center Bonds
Boron can also form three-center bonds with other elements, such as hydrogen and carbon. Three-center bonds are formed when a boron atom shares one pair of electrons with two other atoms. These bonds are typically weaker than single and double bonds and are more susceptible to external energy sources.
One example of a three-center bond formed by boron is in the compound diborane (B2H6). In this molecule, the boron atoms form three-center bonds with hydrogen atoms, resulting in a bridged geometry.

h3>Types of Three-Center Bonds
Boron can form different types of three-center bonds, including:
- B-H-B bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals along the bond axis.
- B-C-B bonds: These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals perpendicular to the bond axis.
In conclusion, boron can form a variety of bonds with other elements, including single bonds, double bonds, and three-center bonds. These bonds are formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals and can result in different geometries and properties.
We invite you to share your thoughts and questions about boron bonds in the comments section below. Do you have any experience working with boron or its compounds? Share your stories and expertise with us!
h2>What's Next?
In our next article, we will explore the properties and applications of boron and its compounds. From its use in semiconductors to its role in medicine, boron is an element with a wide range of applications.
Stay tuned for more articles about chemistry and materials science. Follow us on social media to stay up-to-date with the latest news and updates.
FAQ Section
What is boron?
+Boron is a chemical element with the symbol B and atomic number 5. It is a metalloid and is found in small amounts in many types of rocks and minerals.
What are some common compounds of boron?
+Some common compounds of boron include borane (BH3), boron oxide (B2O3), and diborane (B2H6).
What are some applications of boron?
+Boron has a wide range of applications, including its use in semiconductors, medicine, and materials science.