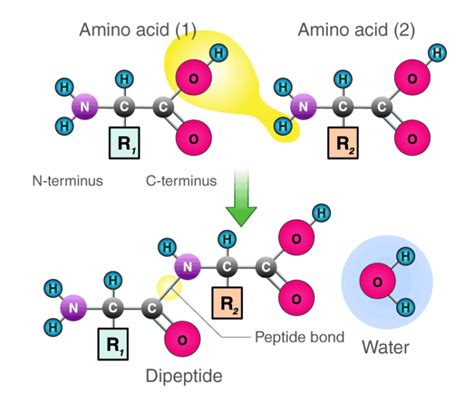
The process of forming peptide bonds is a fundamental aspect of biochemistry, playing a crucial role in the creation of proteins, which are the building blocks of life. Peptide bonds are the chemical links that hold amino acids together, forming a polypeptide chain. Understanding how these bonds are formed is essential for grasping the intricacies of protein synthesis and the biology of living organisms.
The process of forming peptide bonds is a complex one, involving multiple steps and various molecules. However, by breaking down the process into its constituent parts, we can gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms involved. In this article, we will delve into the world of peptide bond formation, exploring the step-by-step process and the key players involved.
The Basics of Peptide Bond Formation
Before diving into the specifics, it's essential to understand the basics of peptide bond formation. A peptide bond is a type of covalent bond that forms between the carboxyl group of one amino acid and the amino group of another. This bond is formed through a dehydration reaction, where a water molecule is released as a byproduct.

Step 1: Amino Acid Activation
The first step in forming a peptide bond is the activation of the amino acid. This involves the attachment of an amino acid to a transfer RNA (tRNA) molecule. The tRNA molecule acts as a molecular adapter, linking the amino acid to the ribosome, where protein synthesis takes place.
The activation of the amino acid is catalyzed by an enzyme called aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. This enzyme ensures that the correct amino acid is attached to the correct tRNA molecule, which is essential for maintaining the accuracy of protein synthesis.
Step 2: Translation Initiation
Once the amino acid is activated, the next step is translation initiation. This involves the binding of the tRNA molecule to the ribosome, positioning the amino acid for peptide bond formation.
Translation initiation is catalyzed by initiation factors, which help to recruit the ribosome and position the tRNA molecule correctly. This step is crucial for ensuring that protein synthesis begins at the correct location and that the polypeptide chain is synthesized in the correct order.
Step 3: Peptide Bond Formation
The next step is the formation of the peptide bond itself. This involves the reaction between the carboxyl group of the first amino acid and the amino group of the second amino acid.
The peptide bond is formed through a dehydration reaction, where a water molecule is released as a byproduct. This reaction is catalyzed by the ribosome, which positions the amino acids correctly and facilitates the reaction.

Step 4: Translocation
Once the peptide bond is formed, the next step is translocation. This involves the movement of the ribosome along the mRNA molecule, positioning the next amino acid for peptide bond formation.
Translocation is catalyzed by elongation factors, which help to move the ribosome and position the next amino acid correctly. This step is essential for ensuring that the polypeptide chain is synthesized in the correct order.
Step 5: Translation Elongation
The final step is translation elongation. This involves the repeated formation of peptide bonds between amino acids, resulting in the synthesis of a polypeptide chain.
Translation elongation is catalyzed by elongation factors, which help to position the amino acids correctly and facilitate the formation of peptide bonds. This step is crucial for ensuring that the polypeptide chain is synthesized accurately and efficiently.
The Importance of Peptide Bond Formation
Peptide bond formation is a critical aspect of biochemistry, playing a central role in the synthesis of proteins. Proteins are the building blocks of life, and their proper synthesis is essential for maintaining the structure and function of living organisms.
Without peptide bond formation, proteins would not be able to form, and life as we know it would not be possible. This highlights the importance of understanding the mechanisms involved in peptide bond formation and the role that this process plays in maintaining the biology of living organisms.
Conclusion: Unraveling the Mystery of Peptide Bond Formation
In conclusion, peptide bond formation is a complex process that involves multiple steps and various molecules. By understanding the mechanisms involved, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the biology of living organisms and the importance of protein synthesis.
Whether you're a student of biochemistry or simply interested in the intricacies of life, understanding peptide bond formation is essential for grasping the complexities of biology. So, take the time to explore this fascinating topic and unravel the mystery of peptide bond formation.
Call to Action
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of peptide bond formation. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Additionally, if you'd like to learn more about the biology of living organisms, we encourage you to explore our other articles on biochemistry and molecular biology.
What is peptide bond formation?
+Peptide bond formation is the process by which amino acids are linked together to form a polypeptide chain. This process is essential for the synthesis of proteins, which are the building blocks of life.
What are the steps involved in peptide bond formation?
+The steps involved in peptide bond formation include amino acid activation, translation initiation, peptide bond formation, translocation, and translation elongation.
Why is peptide bond formation important?
+Peptide bond formation is essential for the synthesis of proteins, which are necessary for maintaining the structure and function of living organisms.