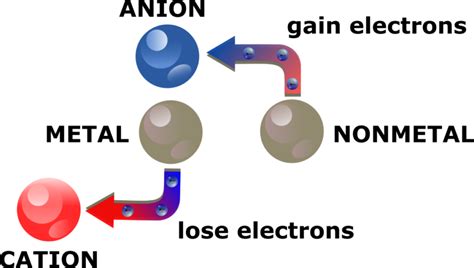
Metals are an essential part of our daily lives, and their ability to form ions is a crucial aspect of their behavior. Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. In this article, we will explore three ways metals form ions, including ionization, oxidation, and dissolution.
Ionization of Metals
Ionization is the process by which a metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion. This occurs when a metal is exposed to high temperatures, electrical discharges, or radiation. The energy required to remove an electron from a metal atom is known as the ionization energy. Different metals have different ionization energies, which depend on the number of electrons in the outermost energy level of the atom.
For example, sodium (Na) has a low ionization energy of 5.14 eV, which means it easily loses an electron to form a positively charged ion (Na+). On the other hand, aluminum (Al) has a higher ionization energy of 13.6 eV, making it more difficult to remove an electron.

Oxidation of Metals
Oxidation is another way metals form ions. Oxidation occurs when a metal reacts with oxygen or another oxidizing agent, resulting in the loss of one or more electrons. This process is often accompanied by a change in color, texture, or other physical properties of the metal.
For example, when iron (Fe) is exposed to air, it reacts with oxygen to form iron oxide (Fe2O3), also known as rust. In this reaction, the iron atom loses three electrons to form a positively charged ion (Fe3+).

Dissolution of Metals
Dissolution is the process by which a metal dissolves in a solvent, such as water or acid, to form ions. This occurs when the metal reacts with the solvent, resulting in the breakdown of the metal's crystal structure and the release of ions.
For example, when sodium chloride (NaCl) is dissolved in water, the sodium ions (Na+) and chloride ions (Cl-) are released into the solution. This process is essential for many industrial applications, including the production of chemicals and pharmaceuticals.

Importance of Metal Ions
Metal ions play a crucial role in many areas of science and technology, including chemistry, biology, and materials science. They are essential for many industrial processes, including the production of chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and electronics.
Metal ions are also important in biological systems, where they play a crucial role in many cellular processes, including enzyme catalysis, protein structure, and cell signaling.

Applications of Metal Ions
Metal ions have many practical applications in various fields, including:
- Catalysis: Metal ions are used as catalysts in many industrial processes, including the production of chemicals and pharmaceuticals.
- Electronics: Metal ions are used in the production of electronic devices, including transistors, diodes, and solar cells.
- Biology: Metal ions play a crucial role in many biological processes, including enzyme catalysis, protein structure, and cell signaling.

Conclusion
In conclusion, metals form ions through three main processes: ionization, oxidation, and dissolution. Metal ions play a crucial role in many areas of science and technology, including chemistry, biology, and materials science. They are essential for many industrial processes and have many practical applications in various fields.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of how metals form ions and their importance in various fields. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is ionization of metals?
+Ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. Ionization is the process by which a metal atom loses one or more electrons to form a positively charged ion.
What is oxidation of metals?
+Oxidation is another way metals form ions. Oxidation occurs when a metal reacts with oxygen or another oxidizing agent, resulting in the loss of one or more electrons.
What is dissolution of metals?
+Dissolution is the process by which a metal dissolves in a solvent, such as water or acid, to form ions. This occurs when the metal reacts with the solvent, resulting in the breakdown of the metal's crystal structure and the release of ions.