Great apes, which include chimpanzees, gorillas, orangutans, and humans, are among the most fascinating creatures in the animal kingdom. Their impressive physical characteristics and advanced cognitive abilities set them apart from other primates and animals. However, what makes great apes truly remarkable is their unique body form, which has evolved over millions of years to adapt to their environments and lifestyles.
The Significance of Great Ape Form

The study of great ape form is crucial for understanding their behavior, ecology, and evolution. By examining their physical characteristics, researchers can gain insights into their adaptations, limitations, and potential vulnerabilities. Furthermore, studying great ape form can provide valuable information for conservation efforts, as it can help identify key factors that influence their survival and well-being.
Characteristics of Great Ape Form
Great apes share several distinct physical characteristics that define their body form. Here are five key characteristics that are common to all great apes:
1. Large Body Size
Great apes are among the largest primates, with adult males weighing between 40-200 kg (88-441 lbs). Their large body size is likely an adaptation for their diet and lifestyle, as it allows them to support their energy needs and protect themselves from predators.
2. Upright Posture
Great apes are characterized by their upright posture, which is facilitated by their flexible spine and pelvis. This posture allows them to walk on two legs, freeing their hands for other activities such as tool use and communication.
3. Advanced Limb Structure
Great apes have advanced limb structures that enable them to move efficiently and manipulate objects with precision. Their arms and hands are adapted for climbing, grasping, and manipulating, while their legs are designed for walking and running.
4. Brain Size and Complexity
Great apes have large and complex brains, which are likely adaptations for their advanced cognitive abilities. Their brains are capable of supporting complex social behaviors, problem-solving, and communication.
5. Specialized Facial Features
Great apes have distinct facial features that are adapted for communication and social interaction. Their faces are characterized by a flat nose, prominent jaw, and expressive eyes, which are capable of conveying a wide range of emotions and intentions.
Adaptations of Great Ape Form
Great ape form has evolved to adapt to their environments and lifestyles. Here are some examples of adaptations that are specific to each great ape species:
Chimpanzees
Chimpanzees have a slender build and long arms, which are adapted for climbing and arboreal locomotion. Their hands are also specialized for tool use, with a flexible wrist and opposable thumb.
Gorillas
Gorillas have a more robust build than chimpanzees, with a larger body size and more muscular limbs. Their arms are shorter than those of chimpanzees, but their hands are more powerful and adapted for terrestrial locomotion.
Orangutans
Orangutans have a unique body form that is adapted for arboreal locomotion. Their arms are long and slender, with a flexible wrist and opposable thumb. Their hands are also specialized for grasping and manipulating branches.
Humans
Humans have a distinctive body form that is adapted for bipedal locomotion. Their legs are longer than those of other great apes, with a more efficient gait and a specialized pelvis and spine. Their hands are also adapted for tool use and manipulation, with a flexible wrist and opposable thumb.
Evolution of Great Ape Form
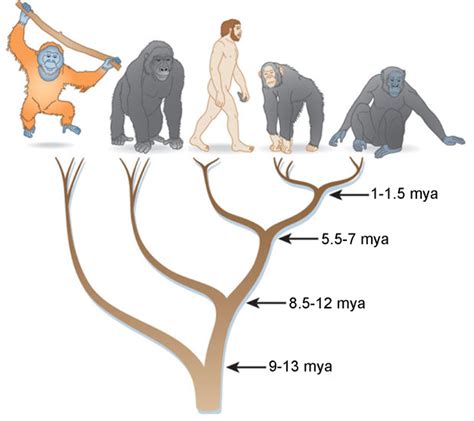
The evolution of great ape form is a complex and still somewhat mysterious process. However, researchers believe that great apes evolved from a common ancestor that lived around 6-8 million years ago. This ancestor is thought to have been a small, ape-like creature that lived in Africa.
Over time, this ancestral population evolved into different species, each with its unique body form and adaptations. The evolution of great ape form was likely driven by a combination of factors, including climate change, dietary shifts, and social competition.
Conservation Implications of Great Ape Form
The study of great ape form has important implications for conservation efforts. By understanding the adaptations and limitations of great ape body form, researchers can identify key factors that influence their survival and well-being.
For example, the loss of habitat and fragmentation of populations can have significant impacts on great ape populations, particularly those with specialized adaptations for arboreal locomotion. Climate change can also affect great ape populations, particularly those that are adapted to specific temperature and precipitation regimes.
Conclusion
Great ape form is a fascinating and complex topic that has important implications for our understanding of their behavior, ecology, and evolution. By studying their physical characteristics and adaptations, researchers can gain insights into their lives and identify key factors that influence their survival and well-being.
We hope that this article has provided a comprehensive overview of great ape form and its significance. We encourage readers to share their thoughts and questions in the comments section below.
What is the significance of great ape form?
+The study of great ape form is crucial for understanding their behavior, ecology, and evolution. It can provide valuable information for conservation efforts and help identify key factors that influence their survival and well-being.
What are the five key characteristics of great ape form?
+The five key characteristics of great ape form are large body size, upright posture, advanced limb structure, brain size and complexity, and specialized facial features.
How has great ape form evolved over time?
+The evolution of great ape form is a complex and still somewhat mysterious process. However, researchers believe that great apes evolved from a common ancestor that lived around 6-8 million years ago.