The electron configuration of an atom is a crucial concept in chemistry and physics, as it helps us understand the arrangement of electrons within an atom. In this article, we will delve into the gold electron configuration, exploring its intricacies and significance.

What is Electron Configuration?
Electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons within an atom, which is determined by the number of protons in the nucleus and the energy levels or shells that the electrons occupy. The electrons are arranged in a specific pattern, with each shell having a limited capacity to hold electrons. The electron configuration of an atom is a crucial factor in determining its chemical properties and behavior.
Understanding the Aufbau Principle and the Pauli Exclusion Principle
To understand the electron configuration of gold, we need to grasp two fundamental principles: the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle. The Aufbau principle states that electrons occupy the lowest available energy levels in an atom, while the Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of quantum numbers.
Gold Electron Configuration: The Basics
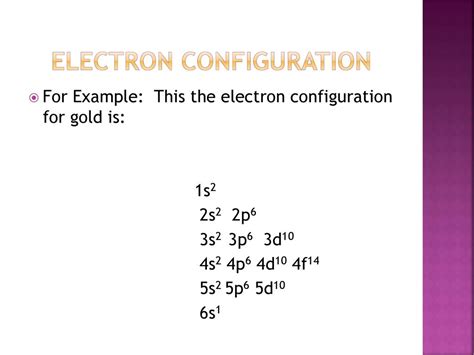
Gold is a chemical element with the atomic number 79 and the symbol Au. Its electron configuration can be written as:
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p⁶ 6s¹ 4f¹⁴ 5d¹⁰

Breaking Down the Gold Electron Configuration
Let's break down the gold electron configuration into its components:
- The first energy level (n=1) contains two electrons in the 1s orbital.
- The second energy level (n=2) contains eight electrons: two in the 2s orbital and six in the 2p orbitals.
- The third energy level (n=3) contains 18 electrons: two in the 3s orbital, six in the 3p orbitals, and ten in the 3d orbitals.
- The fourth energy level (n=4) contains 32 electrons: two in the 4s orbital, six in the 4p orbitals, and ten in the 4d orbitals.
- The fifth energy level (n=5) contains 14 electrons: two in the 5s orbital, six in the 5p orbitals, and six in the 4f orbitals.
- The sixth energy level (n=6) contains one electron in the 6s orbital.
Significance of Gold Electron Configuration
The gold electron configuration is significant in understanding the chemical properties of gold. The arrangement of electrons in gold determines its:
- High ductility and malleability
- High melting point
- Low reactivity
- Ability to form ions and compounds

Applications of Gold Electron Configuration
The gold electron configuration has numerous applications in:
- Electronics: Gold's high conductivity and resistance to corrosion make it an ideal material for electronic components.
- Jewelry: Gold's attractive color and durability make it a popular choice for jewelry.
- Catalysis: Gold's unique electron configuration makes it an effective catalyst for certain chemical reactions.
- Medical applications: Gold's biocompatibility and non-toxicity make it suitable for medical implants and diagnostic equipment.
Conclusion: Unraveling the Mysteries of Gold Electron Configuration
In conclusion, the gold electron configuration is a complex and fascinating topic that helps us understand the chemical properties and behavior of gold. By grasping the Aufbau principle and the Pauli exclusion principle, we can better comprehend the arrangement of electrons in gold and its significance in various applications. Whether you're a chemistry enthusiast or simply curious about the world around you, the gold electron configuration is sure to captivate and inspire.

Get Involved and Share Your Thoughts!
We'd love to hear your thoughts on the gold electron configuration! Do you have any questions or insights to share? Leave a comment below or share this article with your friends and family to spark a discussion.
What is the atomic number of gold?
+The atomic number of gold is 79.
What is the electron configuration of gold?
+The electron configuration of gold is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d¹⁰ 4p⁶ 5s² 4d¹⁰ 5p⁶ 6s¹ 4f¹⁴ 5d¹⁰.
What are some common applications of gold?
+Gold has numerous applications in electronics, jewelry, catalysis, and medical applications.