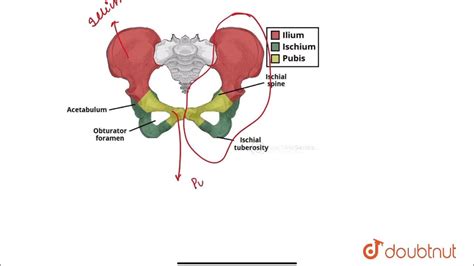
The coxal bone, also known as the hip bone, is a vital part of the human skeletal system. It plays a crucial role in supporting the body's weight, facilitating movement, and protecting internal organs. The coxal bone is formed through a process called fusion, where three separate bones - the ilium, ischium, and pubis - merge to create a single, solid bone. This process occurs during childhood and adolescence, and it is essential for the development of a strong and functional pelvis.
Understanding the formation of the coxal bone through fusion is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it helps us appreciate the complexity and beauty of the human body. Secondly, it provides valuable insights into the development and growth of the skeletal system. Finally, it helps us understand various medical conditions and injuries that affect the coxal bone, such as hip dysplasia, osteoarthritis, and fractures.
In this article, we will delve into the details of the coxal bone's formation through fusion, exploring the processes involved, the timing of fusion, and the factors that influence it. We will also discuss the importance of the coxal bone in the human body and the consequences of fusion failures or abnormalities.
Embryological Development of the Coxal Bone

The coxal bone begins to form during embryonic development, around the 4th to 6th week of gestation. At this stage, the three separate bones - the ilium, ischium, and pubis - are cartilaginous structures that eventually ossify and fuse together. The ilium is the largest of the three bones, forming the upper part of the coxal bone. The ischium forms the lower part, while the pubis forms the front part.
During fetal development, the three bones are separated by cartilaginous joints. As the fetus grows, the bones start to ossify, and the cartilaginous joints begin to close. By birth, the three bones are still separate, but they start to fuse together during childhood and adolescence.
Timing of Fusion
The timing of fusion varies among individuals, but it typically occurs between 10 to 14 years of age. The ilium and ischium start to fuse first, followed by the fusion of the pubis to the ilium and ischium. The entire process of fusion is usually complete by the age of 18.
Factors that influence the timing of fusion include genetics, nutrition, and hormonal levels. For example, individuals with a family history of delayed fusion may experience a similar delay in their own development. Similarly, adequate nutrition and hormonal balance are essential for proper bone growth and fusion.
Factors Affecting Fusion

Several factors can affect the fusion of the coxal bone, including:
- Genetics: As mentioned earlier, genetic factors can influence the timing of fusion.
- Nutrition: Adequate nutrition, particularly calcium and vitamin D, is essential for bone growth and fusion.
- Hormonal balance: Hormones such as growth hormone and thyroid hormone play a crucial role in regulating bone growth and fusion.
- Injuries or trauma: Severe injuries or trauma to the coxal bone can disrupt the fusion process.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as hip dysplasia or osteogenesis imperfecta, can affect the fusion of the coxal bone.
Abnormalities in the fusion process can lead to various medical conditions, including hip dysplasia, osteoarthritis, and fractures.
Importance of the Coxal Bone
The coxal bone plays a vital role in the human body, providing:
- Support: The coxal bone supports the body's weight and facilitates movement.
- Protection: The coxal bone protects internal organs, such as the reproductive organs and the urinary bladder.
- Attachment: The coxal bone serves as an attachment point for various muscles, tendons, and ligaments.
In summary, the coxal bone is a crucial part of the human skeletal system, and its formation through fusion is a complex process that involves the integration of multiple bones. Understanding the factors that influence fusion is essential for appreciating the development and growth of the skeletal system.
Medical Conditions Affecting the Coxal Bone

Several medical conditions can affect the coxal bone, including:
- Hip dysplasia: A condition where the hip joint forms abnormally, leading to instability and potential arthritis.
- Osteoarthritis: A degenerative joint disease that affects the coxal bone and surrounding joints.
- Fractures: Breaks in the coxal bone can occur due to injuries or trauma.
- Osteogenesis imperfecta: A genetic disorder that affects bone growth and density, leading to increased risk of fractures.
These medical conditions can be caused by various factors, including genetic predisposition, injuries, or degenerative processes.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing medical conditions affecting the coxal bone typically involves imaging tests, such as X-rays or MRI scans. Treatment options vary depending on the condition, but may include:
- Physical therapy: To improve mobility and strength.
- Pain management: To alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Surgery: To repair or replace damaged joints or bones.
- Lifestyle modifications: To reduce the risk of further injury or degeneration.
In conclusion, the coxal bone is a vital part of the human skeletal system, and its formation through fusion is a complex process that involves the integration of multiple bones. Understanding the factors that influence fusion is essential for appreciating the development and growth of the skeletal system. By recognizing the importance of the coxal bone and the medical conditions that can affect it, we can take steps to maintain a healthy and functional pelvis.
We hope you found this article informative and engaging. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Share this article with others who may be interested in learning more about the coxal bone and its formation through fusion.
What is the coxal bone?
+The coxal bone, also known as the hip bone, is a vital part of the human skeletal system. It plays a crucial role in supporting the body's weight, facilitating movement, and protecting internal organs.
How is the coxal bone formed?
+The coxal bone is formed through a process called fusion, where three separate bones - the ilium, ischium, and pubis - merge to create a single, solid bone.
What are some medical conditions that can affect the coxal bone?
+Several medical conditions can affect the coxal bone, including hip dysplasia, osteoarthritis, fractures, and osteogenesis imperfecta.