Attachment is a fundamental concept in psychology that refers to the way we form close relationships with others. It's a vital aspect of human development, influencing our emotional well-being, relationships, and overall mental health. In this article, we'll delve into the different forms of attachment, exploring their characteristics, effects, and implications.

What is Attachment?
Attachment is a deep and enduring emotional bond that we form with others, typically beginning in early childhood with our caregivers. This attachment style shapes our expectations, perceptions, and behaviors in relationships throughout our lives. Attachment is not just about love; it's about feeling safe, secure, and valued.
Attachment Theories
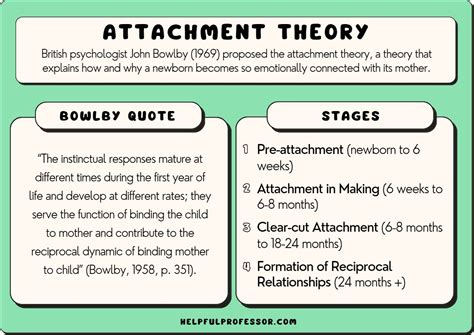
Attachment theories were first introduced by John Bowlby and Mary Ainsworth in the mid-20th century. They proposed that attachment is an evolutionary adaptation that ensures the survival of the species. The attachment system is activated when we feel threatened, scared, or in need of comfort, triggering a response from our caregivers.

Forms of Attachment
There are four primary forms of attachment: secure, anxious, avoidant, and disorganized. Each style is shaped by our early experiences with caregivers and influences our relationships in distinct ways.
Secure Attachment
Securely attached individuals feel comfortable with intimacy, can regulate their emotions effectively, and maintain a sense of independence. They tend to have healthy, fulfilling relationships and are more resilient to stress.
- Characteristics:
- Trusting and open
- Emotionally intelligent
- Good communication skills
- Ability to regulate emotions
- Effects:
- Healthy relationships
- Emotional resilience
- Better stress management

Anxious-Preoccupied Attachment
Those with an anxious-preoccupied attachment style are overly dependent on their partners and fear rejection. They're often clingy, needy, and require constant reassurance.
- Characteristics:
- Fearful of abandonment
- Emotionally intense
- High need for reassurance
- Difficulty with emotional regulation
- Effects:
- Unhealthy relationship dynamics
- Increased stress and anxiety
- Difficulty with emotional intimacy

Dismissive-Avoidant Attachment
Individuals with a dismissive-avoidant attachment style tend to avoid intimacy and emotional connection. They prioritize independence and may come across as aloof or distant.
- Characteristics:
- Fearful of intimacy
- Emotionally reserved
- Prioritize independence
- Difficulty with emotional expression
- Effects:
- Difficulty with intimacy
- Increased stress and anxiety
- Unhealthy relationship dynamics

Disorganized-Disoriented Attachment
Those with a disorganized-disoriented attachment style often exhibit a mix of anxious and avoidant behaviors. They may struggle with emotional regulation, intimacy, and trust.
- Characteristics:
- Difficulty with emotional regulation
- Fearful of intimacy and abandonment
- Disorganized and inconsistent behavior
- Effects:
- Difficulty with emotional intimacy
- Increased stress and anxiety
- Unhealthy relationship dynamics

Implications and Effects of Attachment Styles
Our attachment style influences various aspects of our lives, including relationships, emotional well-being, and mental health. Understanding our attachment style can help us:
- Recognize patterns in our relationships
- Identify areas for personal growth and improvement
- Develop healthier relationship dynamics
- Improve emotional regulation and resilience
Changing Your Attachment Style
While our attachment style is shaped by early experiences, it's not fixed. We can work to change and improve our attachment style through:
- Self-reflection and awareness
- Therapy and counseling
- Healthy relationship experiences
- Emotional regulation and mindfulness practices

Conclusion
Understanding attachment styles is essential for building and maintaining healthy relationships, emotional well-being, and mental health. By recognizing our attachment style and working to improve it, we can develop more fulfilling relationships and improve our overall quality of life.
We hope this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of attachment styles and their implications. Share your thoughts and experiences with attachment styles in the comments below!
What is attachment?
+Attachment is a deep and enduring emotional bond that we form with others, typically beginning in early childhood with our caregivers.
What are the four primary forms of attachment?
+The four primary forms of attachment are secure, anxious, avoidant, and disorganized.
Can I change my attachment style?
+Yes, while our attachment style is shaped by early experiences, it's not fixed. We can work to change and improve our attachment style through self-reflection, therapy, and healthy relationship experiences.