As the tax season unfolds, individuals and businesses alike are tasked with navigating the complexities of tax forms and calculations. One of the most crucial and often misunderstood aspects of tax compliance is the penalty calculation for underpayment of estimated taxes, as outlined in Form 2210. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Form 2210 Line 8, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding the penalty calculations and helping you avoid costly errors.
The Importance of Estimated Tax Payments

The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires taxpayers to make estimated tax payments throughout the year if they expect to owe more than $1,000 in taxes. This includes self-employed individuals, freelancers, and businesses that do not have taxes withheld from their income. Failure to make these payments or underpaying can result in penalties, which is where Form 2210 comes into play.
Understanding Form 2210 Line 8
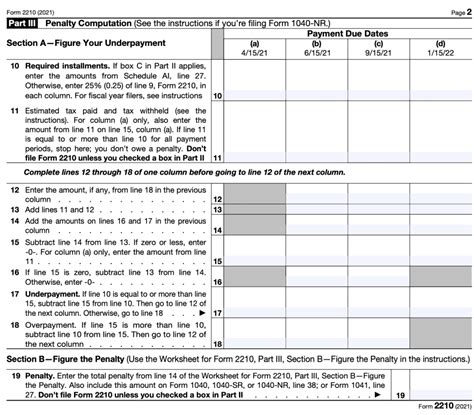
Form 2210 is used to calculate the penalty for underpayment of estimated taxes. Line 8 specifically deals with the calculation of the penalty amount. To accurately complete this line, you must first determine the total underpayment amount, which is the difference between the required estimated tax payments and the actual payments made.
Penalty Calculation Methods
There are two methods for calculating the penalty: the Regular Method and the Annualized Estimated Tax Worksheet. The Regular Method is used if you owe less than $1,000 in penalties, while the Annualized Estimated Tax Worksheet is used for larger underpayments.
Regular Method
The Regular Method involves calculating the penalty based on the total underpayment amount. You will need to complete Form 2210, Part III, to determine the penalty amount. The penalty is calculated as follows:
- 3.25% of the underpayment amount for each quarter, or
- The net earnings from self-employment, whichever is less.
Annualized Estimated Tax Worksheet
The Annualized Estimated Tax Worksheet is used for larger underpayments and takes into account the taxpayer's annualized income. This method is more complex and requires you to calculate your annualized income and estimated tax liability.

Penalty Calculation Steps
To calculate the penalty, follow these steps:
- Determine the total underpayment amount.
- Choose the calculation method (Regular or Annualized Estimated Tax Worksheet).
- Complete Form 2210, Part III (Regular Method) or the Annualized Estimated Tax Worksheet.
- Calculate the penalty amount based on the chosen method.
Avoiding Penalties: Strategies and Best Practices
While navigating Form 2210 Line 8 can be complex, there are strategies to help minimize or avoid penalties altogether. Here are some best practices to keep in mind:
- Make timely estimated tax payments throughout the year.
- Adjust your withholding amounts if you're an employee.
- Consider hiring a tax professional to ensure accurate calculations.
- Keep accurate records of your income and expenses.
Common Errors to Avoid
When completing Form 2210 Line 8, it's essential to avoid common errors that can result in incorrect penalty calculations. Some of these errors include:
- Failing to account for all underpayment amounts.
- Using the wrong calculation method.
- Not considering all sources of income.
- Not keeping accurate records.

Conclusion: Take Control of Your Tax Obligations
Navigating Form 2210 Line 8 requires attention to detail and a thorough understanding of the penalty calculation methods. By following the steps outlined in this article, you'll be better equipped to accurately complete Form 2210 and avoid costly penalties. Remember to stay on top of your estimated tax payments and keep accurate records to ensure a smooth tax season.
Call to Action: Share Your Thoughts
We'd love to hear from you! Share your experiences with Form 2210 Line 8 in the comments below. Do you have any questions or concerns about the penalty calculation methods? Let's start a conversation!
What is the purpose of Form 2210?
+Form 2210 is used to calculate the penalty for underpayment of estimated taxes.
What is the difference between the Regular Method and the Annualized Estimated Tax Worksheet?
+The Regular Method is used for smaller underpayments, while the Annualized Estimated Tax Worksheet is used for larger underpayments and takes into account the taxpayer's annualized income.
How can I avoid penalties for underpayment of estimated taxes?
+Make timely estimated tax payments throughout the year, adjust your withholding amounts if you're an employee, and consider hiring a tax professional to ensure accurate calculations.