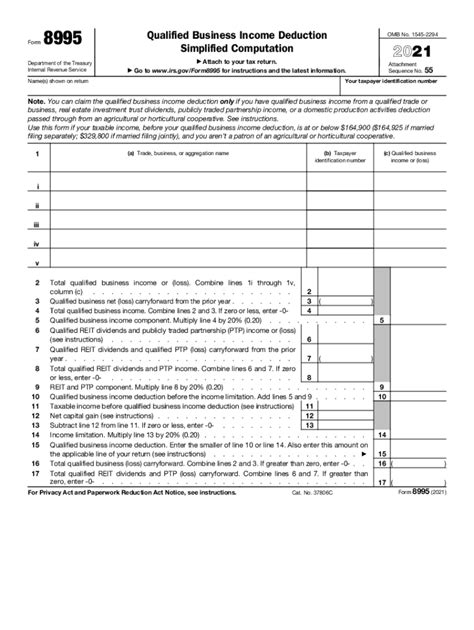
Filling out federal forms can be a daunting task, especially when it comes to complex forms like the Form 8995. The Form 8995 is used to calculate the qualified business income (QBI) deduction, which is a significant tax benefit for eligible self-employed individuals and pass-through entities. In this article, we will break down the Form 8995 into manageable sections and provide guidance on how to fill it out accurately.
Understanding the Form 8995
Before we dive into the nitty-gritty of filling out the Form 8995, it's essential to understand what it's used for. The Form 8995 is used to calculate the QBI deduction, which is a non-corporate business income deduction introduced by the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA). The QBI deduction allows eligible self-employed individuals and pass-through entities to deduct up to 20% of their qualified business income.

Who is Eligible for the QBI Deduction?
To be eligible for the QBI deduction, you must be a self-employed individual or a pass-through entity, such as a partnership, S corporation, or sole proprietorship. Additionally, your business must be a qualified trade or business, which includes most businesses except for certain service-based businesses, such as healthcare, law, and consulting.
Section 1: Identifying the Business
Section 1 of the Form 8995 requires you to identify the business for which you are claiming the QBI deduction. You will need to provide the following information:
- Business name and address
- Employer Identification Number (EIN)
- Business activity code

What is a Business Activity Code?
A business activity code is a six-digit code used to classify your business activity. You can find the list of business activity codes on the IRS website or in the instructions for the Form 8995.
Section 2: Calculating Qualified Business Income
Section 2 of the Form 8995 requires you to calculate your qualified business income. You will need to report the following information:
- Total business income
- Business deductions
- Qualified business income

What is Qualified Business Income?
Qualified business income includes income from a qualified trade or business, such as:
- Business income from a sole proprietorship
- Business income from a partnership or S corporation
- Rental income from a real estate investment trust (REIT)
However, qualified business income does not include:
- Capital gains and losses
- Dividend and interest income
- Income from a C corporation
Section 3: Calculating the QBI Deduction
Section 3 of the Form 8995 requires you to calculate the QBI deduction. You will need to report the following information:
- Qualified business income
- QBI deduction
- Limitation on QBI deduction

What is the Limitation on QBI Deduction?
The QBI deduction is limited to 20% of your qualified business income. However, if your taxable income exceeds a certain threshold, the QBI deduction may be limited or phased out.
Section 4: Additional Calculations
Section 4 of the Form 8995 requires you to perform additional calculations, such as:
- Calculating the QBI deduction for multiple businesses
- Calculating the QBI deduction for a partnership or S corporation

What if I Have Multiple Businesses?
If you have multiple businesses, you will need to calculate the QBI deduction for each business separately. You can then combine the QBI deductions from each business to calculate your total QBI deduction.
Section 5: Signature and Date
Section 5 of the Form 8995 requires you to sign and date the form. You must sign the form under penalty of perjury, and the date must be the date you signed the form.

We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide to filling out the Form 8995. Remember to carefully review the instructions and seek professional help if you are unsure about any of the calculations.
What is the purpose of the Form 8995?
+The Form 8995 is used to calculate the qualified business income (QBI) deduction, which is a significant tax benefit for eligible self-employed individuals and pass-through entities.
Who is eligible for the QBI deduction?
+To be eligible for the QBI deduction, you must be a self-employed individual or a pass-through entity, such as a partnership, S corporation, or sole proprietorship. Additionally, your business must be a qualified trade or business, which includes most businesses except for certain service-based businesses.
What is qualified business income?
+Qualified business income includes income from a qualified trade or business, such as business income from a sole proprietorship, partnership or S corporation, and rental income from a real estate investment trust (REIT).