The term "emboli" refers to small particles or masses that travel through the bloodstream and can cause blockages or damage to various parts of the body. Understanding the concept of emboli is crucial in the medical field, as it can lead to severe health complications if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the world of emboli and explore five key facts about this complex medical condition.
What is an Embolus?

Before we dive into the five facts about emboli, let's first understand what an embolus is. An embolus is a small particle or mass that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream, potentially causing a blockage or damage to a blood vessel. Emboli can be composed of various materials, including blood clots, fat globules, air bubbles, or even tumor cells.
Fact 1: Emboli Can Cause Life-Threatening Complications

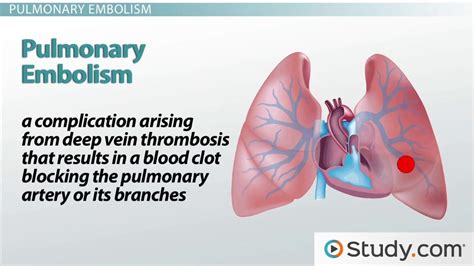
One of the most critical facts about emboli is that they can cause life-threatening complications if left untreated. When an embolus travels through the bloodstream, it can become lodged in a blood vessel, cutting off blood flow to a specific area of the body. This can lead to tissue damage, organ failure, or even death. For example, a pulmonary embolism occurs when an embolus becomes lodged in a blood vessel in the lungs, which can cause severe respiratory distress and even death.
Fact 2: Emboli Can Occur in Various Parts of the Body

Emboli can occur in various parts of the body, including the brain, lungs, heart, and limbs. Depending on the location of the embolus, it can cause different symptoms and complications. For instance, a cerebral embolism occurs when an embolus becomes lodged in a blood vessel in the brain, which can cause stroke-like symptoms, such as weakness, numbness, and difficulty with speech.
Types of Emboli
There are several types of emboli, including:
- Thromboemboli: formed from blood clots
- Fat emboli: formed from fat globules
- Air emboli: formed from air bubbles
- Tumor emboli: formed from tumor cells
Fact 3: Emboli Can Be Caused by Various Factors

Emboli can be caused by various factors, including:
- Blood clots: formed due to injury, surgery, or underlying medical conditions
- Infections: such as endocarditis or sepsis
- Trauma: such as a car accident or fall
- Medical procedures: such as surgery or injections
- Underlying medical conditions: such as cancer, heart disease, or diabetes
Fact 4: Emboli Can Be Diagnosed Using Various Tests

Emboli can be diagnosed using various tests, including:
- Imaging tests: such as CT scans, MRI scans, or ultrasound
- Blood tests: to check for clotting disorders or other underlying conditions
- Angiography: to visualize the blood vessels
- Echocardiography: to visualize the heart
Fact 5: Emboli Can Be Treated with Various Therapies

Emboli can be treated with various therapies, including:
- Anticoagulation therapy: to prevent further clotting
- Thrombolytic therapy: to dissolve existing clots
- Surgical intervention: to remove the embolus
- Supportive care: to manage symptoms and prevent complications
In conclusion, emboli are complex medical conditions that require prompt attention and treatment. By understanding the five facts about emboli, we can better appreciate the importance of seeking medical attention if symptoms persist. If you or someone you know is experiencing symptoms of an embolus, do not hesitate to seek medical help.
What is an embolus?
+An embolus is a small particle or mass that breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream, potentially causing a blockage or damage to a blood vessel.
What are the symptoms of an embolus?
+The symptoms of an embolus depend on the location and severity of the blockage, but may include weakness, numbness, difficulty with speech, and shortness of breath.
How are emboli diagnosed?
+Emboli can be diagnosed using various tests, including imaging tests, blood tests, angiography, and echocardiography.
What is the treatment for an embolus?
+The treatment for an embolus depends on the location and severity of the blockage, but may include anticoagulation therapy, thrombolytic therapy, surgical intervention, and supportive care.
Can emboli be prevented?
+While some emboli cannot be prevented, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk, such as maintaining a healthy weight, exercising regularly, and managing underlying medical conditions.