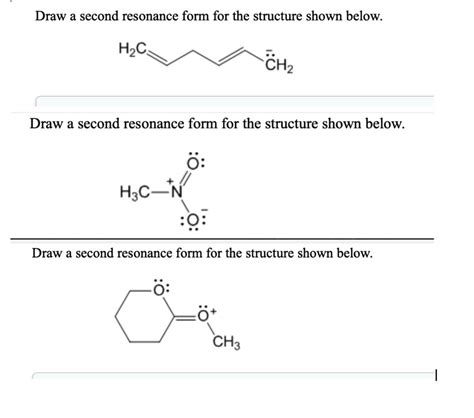
When it comes to understanding and working with chemical structures, being able to draw resonance forms is an essential skill. Resonance forms help us visualize and predict the behavior of molecules, and drawing them can be a powerful tool in understanding chemical reactions and properties. In this article, we will explore the concept of resonance and provide a step-by-step guide on how to draw a second resonance form in 2 easy steps.
Understanding Resonance

Resonance is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us understand the delocalization of electrons within a molecule. It's a way of describing the different possible arrangements of electrons in a molecule, which can lead to different resonance forms. Resonance forms are not real structures, but rather a way of representing the different possible arrangements of electrons in a molecule.
What is a Resonance Form?
A resonance form is a Lewis structure that represents a possible arrangement of electrons in a molecule. Resonance forms are used to describe the delocalization of electrons, which can lead to increased stability and reactivity. By drawing resonance forms, we can visualize the different possible arrangements of electrons in a molecule and predict its behavior.
Step 1: Identify the Conjugated System

The first step in drawing a second resonance form is to identify the conjugated system in the molecule. A conjugated system is a series of alternating double bonds, which can lead to the delocalization of electrons. To identify the conjugated system, look for alternating double bonds in the molecule. This can include double bonds between atoms, as well as lone pairs of electrons that can participate in resonance.
Example: Identifying the Conjugated System
For example, let's consider the molecule benzene (C6H6). Benzene has a conjugated system of alternating double bonds between the carbon atoms. To identify the conjugated system, we can look for the alternating double bonds and lone pairs of electrons that can participate in resonance.
Step 2: Move the Electrons to Form a New Resonance Form

Once we have identified the conjugated system, we can move the electrons to form a new resonance form. To do this, we can move the electrons in the conjugated system to form a new arrangement of double bonds and lone pairs. This can involve moving electrons from one bond to another, or moving lone pairs of electrons to form a new double bond.
Example: Drawing a New Resonance Form
For example, let's consider the molecule benzene (C6H6) again. We can move the electrons in the conjugated system to form a new resonance form. By moving the electrons, we can form a new arrangement of double bonds and lone pairs, which represents a new resonance form.
Benefits of Drawing Resonance Forms

Drawing resonance forms has several benefits in understanding chemistry. By drawing resonance forms, we can:
- Visualize the delocalization of electrons in a molecule
- Predict the stability and reactivity of a molecule
- Understand the different possible arrangements of electrons in a molecule
- Identify the conjugated system in a molecule
Conclusion: Mastering Resonance Forms
Mastering resonance forms is an essential skill in understanding chemistry. By following the 2 easy steps outlined in this article, you can learn to draw a second resonance form and improve your understanding of chemical structures and reactions. Remember to identify the conjugated system and move the electrons to form a new resonance form. With practice, you can become proficient in drawing resonance forms and take your understanding of chemistry to the next level.
What is resonance in chemistry?
+Resonance is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us understand the delocalization of electrons within a molecule. It's a way of describing the different possible arrangements of electrons in a molecule, which can lead to different resonance forms.
What is a resonance form?
+A resonance form is a Lewis structure that represents a possible arrangement of electrons in a molecule. Resonance forms are used to describe the delocalization of electrons, which can lead to increased stability and reactivity.
How do I identify the conjugated system in a molecule?
+To identify the conjugated system, look for alternating double bonds in the molecule. This can include double bonds between atoms, as well as lone pairs of electrons that can participate in resonance.