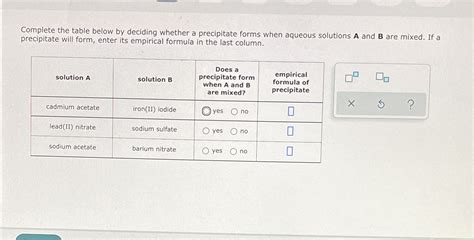
Mixing two substances, A and B, can lead to a chemical reaction that results in the formation of a precipitate. But, what exactly is a precipitate, and under what conditions does it form? In this article, we'll dive into the world of chemistry and explore the concept of precipitation reactions.
What is a Precipitate?

A precipitate is a solid that forms from a solution during a chemical reaction. It's a visible indication that a reaction has occurred, and it can be an essential part of many chemical processes. Precipitates can form through various reactions, including acid-base reactions, oxidation-reduction reactions, and double displacement reactions.
Types of Precipitation Reactions
There are several types of precipitation reactions, including:
- Double displacement reactions: These reactions involve the exchange of ions between two compounds, resulting in the formation of a precipitate.
- Acid-base reactions: These reactions involve the neutralization of an acid and a base, resulting in the formation of a precipitate.
- Oxidation-reduction reactions: These reactions involve the transfer of electrons between two substances, resulting in the formation of a precipitate.
Factors Affecting Precipitate Formation

Several factors can influence the formation of a precipitate when A and B are mixed. These include:
- Concentration: The concentration of the reactants can affect the formation of a precipitate. Increasing the concentration of one or both reactants can increase the likelihood of precipitate formation.
- Temperature: Temperature can also play a role in precipitate formation. Some reactions may require a specific temperature range for precipitation to occur.
- pH: The pH of the solution can affect the formation of a precipitate. Some reactions may require a specific pH range for precipitation to occur.
- Solubility: The solubility of the reactants and products can also affect precipitate formation. If the products are insoluble, they will form a precipitate.
Precipitate Formation and Solubility
The solubility of a substance is a critical factor in determining whether a precipitate will form. If the products of a reaction are insoluble, they will form a precipitate. The solubility of a substance can be affected by various factors, including temperature, pH, and concentration.
- Solubility rules: There are several solubility rules that can help predict whether a substance will form a precipitate. These rules include:
- Most sodium, potassium, and ammonium salts are soluble.
- Most nitrates and acetates are soluble.
- Most chlorides, bromides, and iodides are soluble, except for those of silver, lead, and mercury.
- Most sulfates are soluble, except for those of barium, strontium, and lead.
Examples of Precipitation Reactions

Here are some examples of precipitation reactions:
- Silver nitrate and sodium chloride: When silver nitrate (AgNO3) is mixed with sodium chloride (NaCl), a precipitate of silver chloride (AgCl) forms.
- Calcium chloride and sodium carbonate: When calcium chloride (CaCl2) is mixed with sodium carbonate (Na2CO3), a precipitate of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) forms.
- Copper sulfate and sodium hydroxide: When copper sulfate (CuSO4) is mixed with sodium hydroxide (NaOH), a precipitate of copper hydroxide (Cu(OH)2) forms.
Precipitation Reactions in Everyday Life
Precipitation reactions have many practical applications in everyday life. Some examples include:
- Water treatment: Precipitation reactions are used to remove impurities from water.
- Food industry: Precipitation reactions are used to remove impurities from food products.
- Pharmaceutical industry: Precipitation reactions are used to synthesize pharmaceuticals.
What is a precipitate?
+A precipitate is a solid that forms from a solution during a chemical reaction.
What are the factors that affect precipitate formation?
+The factors that affect precipitate formation include concentration, temperature, pH, and solubility.
What are some examples of precipitation reactions?
+Some examples of precipitation reactions include the reaction between silver nitrate and sodium chloride, calcium chloride and sodium carbonate, and copper sulfate and sodium hydroxide.
In conclusion, the formation of a precipitate when A and B are mixed depends on various factors, including concentration, temperature, pH, and solubility. Understanding precipitation reactions is crucial in many fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science. By recognizing the factors that influence precipitate formation, we can better predict and control the outcome of chemical reactions.
Now, it's your turn! Share your thoughts on precipitation reactions and their applications in the comments below. Do you have any questions or topics you'd like to discuss? Let's get the conversation started!