The world of taxes can be complex and overwhelming, especially for individuals who are self-employed or have other sources of income outside of a traditional salary. One crucial aspect of tax compliance is making quarterly estimated tax payments, which is where the Form 1040-ES comes in. In this article, we'll delve into the world of quarterly tax payments, explaining what Form 1040-ES is, who needs to file it, and how to do so.
What is Form 1040-ES?

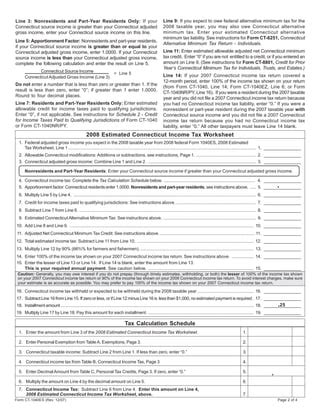
Form 1040-ES is a quarterly estimated tax payment form used by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to collect taxes from individuals who expect to owe $1,000 or more in taxes for the year. This form is typically used by self-employed individuals, freelancers, and small business owners who don't have taxes withheld from their income. By making quarterly payments, individuals can avoid penalties and interest on their tax bill.
Who Needs to File Form 1040-ES?
Not everyone needs to file Form 1040-ES. However, if you fall into one of the following categories, you may need to make quarterly estimated tax payments:
- Self-employed individuals, including freelancers and independent contractors
- Small business owners, including sole proprietors and single-member LLCs
- Individuals with rental income or investment income
- Individuals with retirement income that isn't subject to withholding
- Individuals who expect to owe $1,000 or more in taxes for the year
How to File Form 1040-ES
Filing Form 1040-ES is a relatively straightforward process. Here are the steps to follow:
- Determine Your Tax Liability: Estimate your tax liability for the year by calculating your total income, deductions, and credits. You can use Form 1040-ES to help you estimate your tax liability.
- Choose a Payment Method: You can make quarterly payments online, by phone, or by mail. The IRS offers several payment options, including:
- Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS)
- Online payment through the IRS website
- Phone payment through the IRS
- Mail payment with a check or money order
- Make Quarterly Payments: Quarterly payments are due on April 15th for the first quarter, June 15th for the second quarter, September 15th for the third quarter, and January 15th of the following year for the fourth quarter.
- File Form 1040-ES: You'll need to file Form 1040-ES with each quarterly payment. You can download the form from the IRS website or use tax software to prepare and file the form.
Benefits of Filing Form 1040-ES
Filing Form 1040-ES can help you avoid penalties and interest on your tax bill. Here are some benefits of making quarterly estimated tax payments:
- Avoid Penalties: By making timely quarterly payments, you can avoid penalties and interest on your tax bill.
- Reduce Tax Bill: Making quarterly payments can help reduce your tax bill at the end of the year.
- Improve Cash Flow: By spreading out your tax payments throughout the year, you can improve your cash flow and avoid a large tax bill at the end of the year.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When filing Form 1040-ES, there are several common mistakes to avoid:
- Missing Deadlines: Make sure to make quarterly payments on time to avoid penalties and interest.
- Underestimating Tax Liability: Make sure to accurately estimate your tax liability to avoid penalties and interest.
- Not Keeping Records: Keep accurate records of your quarterly payments, including receipts and payment confirmations.
FAQs
What is the deadline for making quarterly estimated tax payments?
+Quarterly payments are due on April 15th for the first quarter, June 15th for the second quarter, September 15th for the third quarter, and January 15th of the following year for the fourth quarter.
How do I calculate my tax liability for Form 1040-ES?
+You can use Form 1040-ES to estimate your tax liability. You'll need to calculate your total income, deductions, and credits to determine your tax liability.
What are the penalties for not making quarterly estimated tax payments?
+If you don't make quarterly estimated tax payments, you may be subject to penalties and interest on your tax bill. The penalty is typically calculated as a percentage of the unpaid tax, plus interest on the unpaid amount.
Final Thoughts
Filing Form 1040-ES is an important part of tax compliance for self-employed individuals and small business owners. By making quarterly estimated tax payments, you can avoid penalties and interest on your tax bill. Remember to accurately estimate your tax liability, choose a payment method, and file Form 1040-ES on time. If you have any questions or concerns, don't hesitate to reach out to a tax professional for guidance.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive guide to filing Form 1040-ES. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.