Volcanoes are fascinating landforms that have captivated humans for centuries. While many of us associate volcanoes with destructive power, they are also responsible for creating new land and shaping our planet's surface. One of the key factors in volcano formation is plate tectonics, specifically the interaction between moving tectonic plates. In this article, we will delve into the world of volcanology and explore the concept of convergent boundaries and their role in volcano formation.
What are Convergent Boundaries?

Convergent boundaries occur when two or more tectonic plates move towards each other. This process can lead to a variety of geological phenomena, including earthquakes, mountain building, and, in some cases, volcanic activity. At convergent boundaries, the Earth's crust is subjected to immense stress, resulting in the formation of faults, folds, and volcanic arcs.
Types of Convergent Boundaries
There are several types of convergent boundaries, each with distinct characteristics. These include:
- Continental-continental convergent boundaries: where two continental plates collide, resulting in mountain building and faulting.
- Oceanic-continental convergent boundaries: where an oceanic plate collides with a continental plate, often resulting in subduction of the oceanic plate.
- Oceanic-oceanic convergent boundaries: where two oceanic plates converge, resulting in the formation of volcanic arcs.
Volcano Formation at Convergent Boundaries

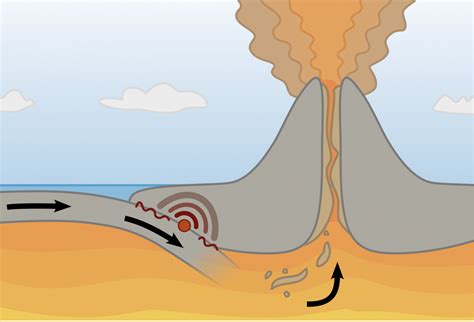
At convergent boundaries, the interaction between tectonic plates can lead to the formation of volcanoes. This occurs when the overlying plate is subjected to increasing heat and pressure, causing the rocks to melt and form magma. As the magma rises through the crust, it can erupt as lava, creating a volcano.
There are several factors that contribute to volcano formation at convergent boundaries:
- Subduction: the process of one plate being forced beneath another, resulting in the formation of a volcanic arc.
- Partial melting: the process of rocks melting due to increasing heat and pressure, resulting in the formation of magma.
- Magma ascent: the process of magma rising through the crust, resulting in volcanic eruptions.
Examples of Volcanoes Formed at Convergent Boundaries
There are numerous examples of volcanoes formed at convergent boundaries around the world. Some notable examples include:
- The Andes mountain range, where the Nazca plate is being subducted beneath the South American plate.
- The Japanese island arc, where the Pacific plate is being subducted beneath the North American plate.
- The Cascade Range in North America, where the Juan de Fuca plate is being subducted beneath the North American plate.
Benefits and Risks of Volcanoes Formed at Convergent Boundaries

Volcanoes formed at convergent boundaries can have both positive and negative impacts on the surrounding environment and human populations.
Benefits:
- Creation of new land: volcanic eruptions can create new landforms, such as volcanic islands and lava flows.
- Mineral deposits: volcanic activity can result in the formation of mineral deposits, such as copper and gold.
- Fertile soil: volcanic ash can create fertile soil, supporting agriculture and plant growth.
Risks:
- Volcanic eruptions: can be destructive and deadly, affecting nearby populations and ecosystems.
- Lahars: mudflows caused by volcanic ash and debris can be devastating, resulting in loss of life and property.
- Ash fall: can affect global climate patterns and cause widespread disruption to air travel and agriculture.
Conclusion: The Importance of Volcanoes Formed at Convergent Boundaries
Volcanoes formed at convergent boundaries play a crucial role in shaping our planet's surface. Understanding the processes that lead to volcano formation is essential for mitigating the risks associated with volcanic activity and appreciating the benefits of these natural wonders.
As we continue to explore the world of volcanology, we are reminded of the awe-inspiring power of geological forces that shape our planet. By studying volcanoes formed at convergent boundaries, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the complex interactions that govern our planet's surface.
What is the difference between a convergent boundary and a divergent boundary?
+A convergent boundary occurs when two or more tectonic plates move towards each other, resulting in subduction, collision, or volcanic activity. A divergent boundary occurs when two or more tectonic plates move apart, resulting in the creation of new crust and the formation of mid-ocean ridges.
What is the most notable example of a volcano formed at a convergent boundary?
+The Andes mountain range is a notable example of a volcanic arc formed at a convergent boundary, where the Nazca plate is being subducted beneath the South American plate.
What are the benefits of volcanoes formed at convergent boundaries?
+Volcanoes formed at convergent boundaries can create new land, result in the formation of mineral deposits, and create fertile soil.