The concept of molecular bonding is a fundamental aspect of chemistry, and understanding the different types of bonds that can form between atoms is crucial for any aspiring chemist. One of the most common types of bonds is the sigma (σ) bond, which is a covalent bond that can form between two atoms. But can p orbitals form sigma bonds? In this article, we will explore the world of molecular orbitals and examine the possibility of p orbitals forming sigma bonds.
The Basics of Sigma Bonds
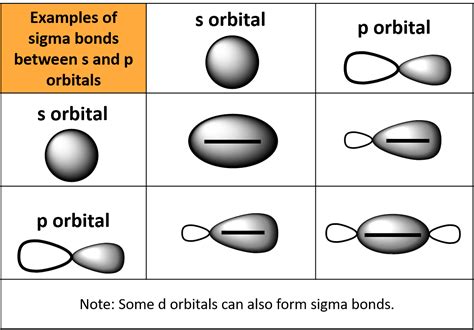
Sigma bonds are a type of covalent bond that forms when two atomic orbitals overlap end-to-end, resulting in a symmetrical, cylindrical shape around the bond axis. Sigma bonds are typically formed between s orbitals, which are spherical in shape, and can also form between s and p orbitals, or between two p orbitals that are oriented in a specific way.
Understanding P Orbitals
P orbitals, also known as p atomic orbitals, are a type of atomic orbital that is dumbbell-shaped, with two lobes of electron density on either side of the nucleus. P orbitals are oriented perpendicular to the bond axis and are typically involved in the formation of pi (π) bonds.
Can P Orbitals Form Sigma Bonds?
Now, let's get to the question at hand: can p orbitals form sigma bonds? The answer is yes, but with some caveats. P orbitals can form sigma bonds, but only under specific conditions.

When two p orbitals are oriented in a specific way, they can overlap end-to-end, resulting in a sigma bond. This can occur when the p orbitals are aligned parallel to each other and perpendicular to the bond axis. In this orientation, the p orbitals can form a sigma bond, which is often referred to as a pσ bond.
Examples of P Orbitals Forming Sigma Bonds
There are several examples of molecules in which p orbitals form sigma bonds. One classic example is the molecule BF3 (boron trifluoride), in which the boron atom forms sigma bonds with the fluorine atoms using its p orbitals.
Another example is the molecule CO2 (carbon dioxide), in which the carbon atom forms sigma bonds with the oxygen atoms using its p orbitals.
Key Conditions for P Orbitals to Form Sigma Bonds
While p orbitals can form sigma bonds, there are some key conditions that must be met:
- The p orbitals must be oriented parallel to each other and perpendicular to the bond axis.
- The p orbitals must be able to overlap end-to-end, resulting in a symmetrical, cylindrical shape around the bond axis.
- The energy levels of the p orbitals must be similar, allowing for effective overlap and bonding.
Conclusion
In conclusion, p orbitals can form sigma bonds under specific conditions. When p orbitals are oriented in a specific way and can overlap end-to-end, they can form a sigma bond, which is often referred to as a pσ bond. This type of bonding is important in many molecules, including BF3 and CO2.
How to Visualize Sigma Bonds Formed by P Orbitals
Visualizing sigma bonds formed by p orbitals can be a bit tricky, but there are several tools and techniques that can help. One way to visualize these bonds is to use molecular modeling software, such as Gaussian or ChemDraw. These programs allow you to visualize the molecular orbitals and bonds in 3D, making it easier to understand the orientation and overlap of the p orbitals.
Another way to visualize sigma bonds formed by p orbitals is to use diagrams and illustrations. By drawing diagrams of the molecular orbitals and bonds, you can get a better sense of how the p orbitals are oriented and how they overlap to form sigma bonds.
The Importance of Sigma Bonds in Chemistry
Sigma bonds are a fundamental aspect of chemistry, and understanding how they form and behave is crucial for any aspiring chemist. Sigma bonds are involved in many chemical reactions and processes, including the formation of molecules, the breaking of bonds, and the transfer of electrons.
By understanding how p orbitals can form sigma bonds, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of molecular bonding.
Future Directions
While we have explored the possibility of p orbitals forming sigma bonds, there is still much to be learned about this topic. Future research could focus on the specific conditions under which p orbitals can form sigma bonds, as well as the implications of this type of bonding for chemical reactions and processes.
In addition, further research could explore the role of sigma bonds in biological systems, where they play a critical role in the formation and function of molecules such as proteins and DNA.
Conclusion
In conclusion, p orbitals can form sigma bonds under specific conditions, and understanding this type of bonding is crucial for any aspiring chemist. By visualizing and understanding the orientation and overlap of p orbitals, you can gain a deeper appreciation for the complexity and beauty of molecular bonding.
Call to Action
We hope that this article has provided you with a deeper understanding of the possibility of p orbitals forming sigma bonds. Whether you are a student, researcher, or simply interested in chemistry, we encourage you to continue exploring the fascinating world of molecular bonding.
Share your thoughts and questions in the comments below!
What are sigma bonds?
+Sigma bonds are a type of covalent bond that forms when two atomic orbitals overlap end-to-end, resulting in a symmetrical, cylindrical shape around the bond axis.
Can p orbitals form sigma bonds?
+Yes, p orbitals can form sigma bonds under specific conditions, such as when they are oriented parallel to each other and perpendicular to the bond axis.
What are some examples of molecules in which p orbitals form sigma bonds?
+Examples include BF3 (boron trifluoride) and CO2 (carbon dioxide), in which the boron and carbon atoms form sigma bonds with the fluorine and oxygen atoms using their p orbitals.