The fascinating world of animal physiology and nutrition! Animals have evolved intricate mechanisms to store energy for future use, much like humans do. One of the most interesting ways animals store energy is in the form of carbohydrates, specifically as glycogen or starch. In this article, we'll delve into the world of animal physiology and explore how animals store carbohydrates as glycogen or starch.
What is Glycogen and Starch?

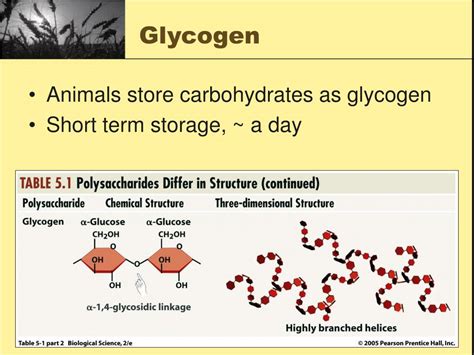
Glycogen and starch are complex carbohydrates that serve as energy storage molecules in animals. Glycogen is a polysaccharide, composed of long chains of glucose molecules, which is stored in the liver and muscles of animals. Starch, on the other hand, is a carbohydrate composed of glucose molecules that are linked together in a long chain. While glycogen is typically stored in animal tissues, starch is often stored in plant cells.
Why Do Animals Store Carbohydrates as Glycogen or Starch?
Animals store carbohydrates as glycogen or starch for several reasons:
- Energy storage: Glycogen and starch serve as energy reserves that can be quickly mobilized when an animal needs it. This is especially important for animals that experience fluctuations in food availability or have high energy demands.
- Rapid energy mobilization: Glycogen and starch can be rapidly broken down into glucose, which can then be used by the animal's cells for energy production.
- Survival during periods of fasting: When food is scarce, animals can rely on their stored glycogen and starch to sustain them until food becomes available again.
How Do Animals Store Carbohydrates as Glycogen or Starch?

The process of storing carbohydrates as glycogen or starch involves several steps:
- Glucose uptake: Glucose is absorbed into the animal's bloodstream from the digestive system.
- Glucose conversion: Glucose is converted into glycogen or starch through a series of enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
- Storage: Glycogen and starch are stored in specific tissues, such as the liver and muscles, or in plant cells.
Key Enzymes Involved in Glycogen and Starch Synthesis
Several key enzymes are involved in the synthesis of glycogen and starch in animals:
- Glycogen synthase: This enzyme catalyzes the transfer of glucose molecules to the growing glycogen chain.
- Branching enzyme: This enzyme creates branches in the glycogen molecule, allowing for more efficient storage.
- Starch synthase: This enzyme catalyzes the transfer of glucose molecules to the growing starch chain.
Examples of Animals That Store Carbohydrates as Glycogen or Starch

Many animals store carbohydrates as glycogen or starch, including:
- Mammals: Humans, dogs, and cats all store glycogen in their livers and muscles.
- Birds: Chickens and other birds store glycogen in their livers and muscles.
- Fish: Some species of fish, such as salmon, store glycogen in their livers and muscles.
- Insects: Some insects, such as bees, store starch in their bodies.
Comparison of Glycogen and Starch Storage in Animals

While both glycogen and starch serve as energy storage molecules in animals, there are some key differences between the two:
- Location: Glycogen is typically stored in animal tissues, while starch is often stored in plant cells.
- Structure: Glycogen is a more branched molecule than starch, allowing for more efficient storage.
- Energy mobilization: Glycogen can be rapidly mobilized for energy production, while starch is often broken down more slowly.
Regulation of Glycogen and Starch Synthesis

The synthesis of glycogen and starch in animals is tightly regulated by several factors, including:
- Hormones: Insulin and glucagon play key roles in regulating glycogen synthesis in animals.
- Energy status: The energy status of the animal can influence the rate of glycogen and starch synthesis.
- Nutrient availability: The availability of glucose and other nutrients can impact the rate of glycogen and starch synthesis.
Conclusion
In conclusion, animals have evolved intricate mechanisms to store energy for future use, including the storage of carbohydrates as glycogen or starch. Understanding how animals store carbohydrates as glycogen or starch can provide valuable insights into animal physiology and nutrition. Whether you're a researcher, animal enthusiast, or simply interested in learning more about the natural world, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the fascinating world of animal carbohydrate storage.
What is the main difference between glycogen and starch?
+The main difference between glycogen and starch is the location of storage. Glycogen is typically stored in animal tissues, while starch is often stored in plant cells.
Why do animals store carbohydrates as glycogen or starch?
+Animals store carbohydrates as glycogen or starch for energy storage, rapid energy mobilization, and survival during periods of fasting.
What are the key enzymes involved in glycogen and starch synthesis?
+The key enzymes involved in glycogen and starch synthesis include glycogen synthase, branching enzyme, and starch synthase.