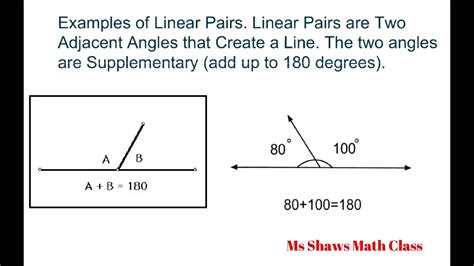
In geometry, angles play a crucial role in understanding the relationships between lines, shapes, and spaces. One such fundamental concept is the linear pair of angles. In this article, we will delve into the definition, properties, and examples of linear pair angles to help you grasp this essential geometric concept.
A linear pair of angles is formed when two lines intersect, creating a pair of adjacent angles that lie on opposite sides of the vertex. These angles are supplementary, meaning their sum is always 180 degrees. Understanding linear pair angles is vital in various geometric applications, such as solving problems involving intersecting lines, angles, and shapes.

Definition of Linear Pair Angles
Linear pair angles are defined as two adjacent angles that lie on opposite sides of a common vertex, formed by the intersection of two lines. These angles are supplementary, meaning their sum is always 180 degrees.
Properties of Linear Pair Angles
The following properties are essential to understanding linear pair angles:
- The two angles are adjacent, meaning they share a common vertex.
- The angles lie on opposite sides of the vertex.
- The sum of the two angles is always 180 degrees.
Examples of Linear Pair Angles
Let's consider a few examples to illustrate the concept of linear pair angles.

- Example 1: In the diagram below, ∠A and ∠B form a linear pair of angles.

In this case, ∠A and ∠B are adjacent angles that lie on opposite sides of the vertex, and their sum is 180 degrees.
- Example 2: In the diagram below, ∠C and ∠D form a linear pair of angles.

In this case, ∠C and ∠D are adjacent angles that lie on opposite sides of the vertex, and their sum is 180 degrees.
Types of Linear Pair Angles
There are several types of linear pair angles, including:
- Adjacent linear pair angles: These are linear pair angles that share a common vertex and lie on opposite sides of the vertex.
- Vertical linear pair angles: These are linear pair angles that are formed by the intersection of two lines and lie on opposite sides of the vertex.
- Supplementary linear pair angles: These are linear pair angles whose sum is 180 degrees.
Real-World Applications of Linear Pair Angles
Linear pair angles have numerous real-world applications, including:
- Architecture: Linear pair angles are used in building design to create structural integrity and stability.
- Engineering: Linear pair angles are used in engineering to design and build complex systems, such as bridges and roads.
- Art: Linear pair angles are used in art to create perspective and depth.
Conclusion
In conclusion, linear pair angles are a fundamental concept in geometry that plays a crucial role in understanding the relationships between lines, shapes, and spaces. By understanding the definition, properties, and examples of linear pair angles, you can develop a deeper appreciation for the intricacies of geometry and its applications in various fields.
If you have any questions or comments about linear pair angles, please don't hesitate to share them below. We would love to hear from you!
What is a linear pair of angles?
+A linear pair of angles is a pair of adjacent angles that lie on opposite sides of a common vertex, formed by the intersection of two lines.
What is the sum of a linear pair of angles?
+The sum of a linear pair of angles is always 180 degrees.
What are some real-world applications of linear pair angles?
+Linear pair angles have numerous real-world applications, including architecture, engineering, and art.