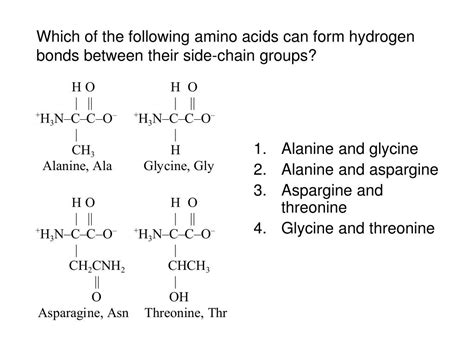
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and they play a crucial role in various biological processes. One of the key characteristics of amino acids is their ability to form hydrogen bonds, which are essential for the stability and structure of proteins. In this article, we will discuss seven amino acids that form hydrogen bonds and their significance in protein structure and function.
Hydrogen Bonding in Amino Acids
Hydrogen bonding is a type of weak electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, and another electronegative atom. In amino acids, hydrogen bonding occurs between the amino group (-NH2) and the carboxyl group (-COOH) or between the amino group and other electronegative atoms.

1. Glycine (Gly)
Glycine is the simplest amino acid, with a single hydrogen atom as its side chain. Despite its simplicity, glycine is capable of forming hydrogen bonds with other amino acids, which is essential for the stability of collagen, a protein found in connective tissue.

2. Alanine (Ala)
Alanine is a non-essential amino acid that plays a crucial role in the structure and function of proteins. Its methyl group (-CH3) is capable of forming weak hydrogen bonds with other electronegative atoms, which helps to stabilize the protein structure.

3. Serine (Ser)
Serine is a polar amino acid that contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) in its side chain. This hydroxyl group is capable of forming strong hydrogen bonds with other electronegative atoms, which is essential for the stability of proteins such as collagen and elastin.

4. Threonine (Thr)
Threonine is another polar amino acid that contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) in its side chain. Its ability to form hydrogen bonds with other electronegative atoms is essential for the stability of proteins such as collagen and elastin.

5. Asparagine (Asn)
Asparagine is a polar amino acid that contains an amide group (-CONH2) in its side chain. This amide group is capable of forming strong hydrogen bonds with other electronegative atoms, which is essential for the stability of proteins such as collagen and elastin.

6. Glutamine (Gln)
Glutamine is a polar amino acid that contains an amide group (-CONH2) in its side chain. Its ability to form hydrogen bonds with other electronegative atoms is essential for the stability of proteins such as collagen and elastin.

7. Histidine (His)
Histidine is a basic amino acid that contains an imidazole ring in its side chain. This imidazole ring is capable of forming strong hydrogen bonds with other electronegative atoms, which is essential for the stability of proteins such as hemoglobin and myoglobin.

Importance of Hydrogen Bonding in Amino Acids
Hydrogen bonding plays a crucial role in the structure and function of proteins. It helps to stabilize the protein structure, facilitate protein-ligand interactions, and enable protein folding and unfolding. The seven amino acids discussed in this article are essential for the formation of hydrogen bonds in proteins, and their ability to form these bonds is critical for various biological processes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hydrogen bonding is an essential property of amino acids that plays a critical role in the structure and function of proteins. The seven amino acids discussed in this article are capable of forming hydrogen bonds with other electronegative atoms, which is essential for the stability and function of proteins. Understanding the importance of hydrogen bonding in amino acids is crucial for the development of new therapeutic strategies and the design of novel biomaterials.
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the importance of hydrogen bonding in amino acids. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them with us.
What is hydrogen bonding in amino acids?
+Hydrogen bonding is a type of weak electrostatic attraction between a hydrogen atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom, such as oxygen, nitrogen, or fluorine, and another electronegative atom.
Which amino acids are capable of forming hydrogen bonds?
+Glycine, alanine, serine, threonine, asparagine, glutamine, and histidine are capable of forming hydrogen bonds with other electronegative atoms.
What is the importance of hydrogen bonding in amino acids?
+Hydrogen bonding plays a crucial role in the structure and function of proteins, helping to stabilize the protein structure, facilitate protein-ligand interactions, and enable protein folding and unfolding.