Proteins are the building blocks of life, and their unique structures and functions are determined by the way amino acids bond together. Amino acids are the fundamental components of proteins, and their bonding patterns play a crucial role in determining the overall properties of proteins. In this article, we will explore the five main ways amino acids bond together to form proteins.

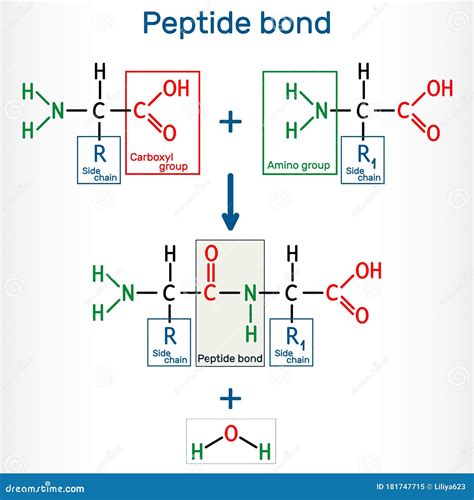
Peptide Bonding: The Primary Linkage
Peptide Bonding: The Primary Linkage
Peptide bonding is the primary linkage between amino acids in a protein. It involves the condensation reaction between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another, resulting in the formation of a peptide bond. This bond is a covalent bond, meaning it involves the sharing of electrons between atoms. Peptide bonding is the most common type of bonding between amino acids and is responsible for the formation of the polypeptide chain.
How Peptide Bonding Occurs
Peptide bonding occurs through a process called dehydration synthesis. In this process, the amino group of one amino acid donates a hydrogen atom, while the carboxyl group of another amino acid donates a hydroxyl group. The resulting peptide bond is a strong covalent bond that holds the amino acids together.
Hydrogen Bonding: The Secondary Structure
Hydrogen Bonding: The Secondary Structure
Hydrogen bonding is a type of weak bonding that occurs between amino acids in a protein. It involves the attraction between the positively charged amino group and the negatively charged carboxyl group of adjacent amino acids. Hydrogen bonding is responsible for the formation of the secondary structure of proteins, including alpha helices and beta sheets.
Types of Hydrogen Bonds
There are two main types of hydrogen bonds: alpha helices and beta sheets. Alpha helices are spiral structures that are stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another. Beta sheets, on the other hand, are flat structures that are stabilized by hydrogen bonds between the amino group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another.

Disulfide Bonding: The Tertiary Structure
Disulfide Bonding: The Tertiary Structure
Disulfide bonding is a type of covalent bonding that occurs between amino acids in a protein. It involves the formation of a sulfur-sulfur bond between the side chains of two cysteine amino acids. Disulfide bonding is responsible for the formation of the tertiary structure of proteins, including the overall shape and folding of the protein.
Importance of Disulfide Bonding
Disulfide bonding plays a crucial role in the stability and function of proteins. It helps to maintain the native conformation of proteins and is involved in the formation of protein-ligand complexes.
Ionic Bonding: The Quaternary Structure
Ionic Bonding: The Quaternary Structure
Ionic bonding is a type of electrostatic bonding that occurs between amino acids in a protein. It involves the attraction between positively charged amino groups and negatively charged carboxyl groups. Ionic bonding is responsible for the formation of the quaternary structure of proteins, including the assembly of multiple polypeptide chains.
Types of Ionic Bonds
There are two main types of ionic bonds: salt bridges and ion pairs. Salt bridges are ionic bonds that occur between amino acids with opposite charges, while ion pairs are ionic bonds that occur between amino acids with the same charge.

Van der Waals Bonding: The Quaternary Structure
Van der Waals Bonding: The Quaternary Structure
Van der Waals bonding is a type of weak bonding that occurs between amino acids in a protein. It involves the attraction between non-polar molecules and is responsible for the formation of the quaternary structure of proteins.
Importance of Van der Waals Bonding
Van der Waals bonding plays a crucial role in the stability and function of proteins. It helps to maintain the native conformation of proteins and is involved in the formation of protein-ligand complexes.
In conclusion, the bonding patterns between amino acids play a crucial role in determining the structure and function of proteins. Understanding the different types of bonding that occur between amino acids can provide valuable insights into the mechanisms of protein folding and function.

Call to Action
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the different ways amino acids bond together to form proteins. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below. Additionally, if you would like to learn more about protein biology, we encourage you to explore our other articles on the subject.
What is the primary linkage between amino acids in a protein?
+The primary linkage between amino acids in a protein is the peptide bond.
What type of bonding is responsible for the formation of the secondary structure of proteins?
+Hydrogen bonding is responsible for the formation of the secondary structure of proteins.
What type of bonding is responsible for the formation of the quaternary structure of proteins?
+Ionic bonding and van der Waals bonding are responsible for the formation of the quaternary structure of proteins.