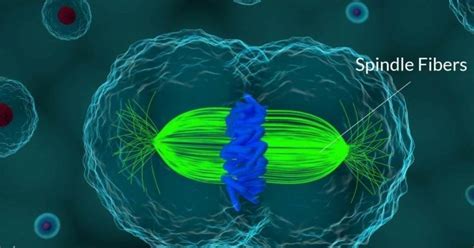
Cell division is a complex process that is crucial for the growth, development, and maintenance of all living organisms. One of the key structures involved in this process is the spindle fiber, a dynamic and highly organized network of microtubules that plays a vital role in the separation of chromosomes during cell division. In this article, we will explore the five ways in which spindle fibers impact cell division.

The Structure and Function of Spindle Fibers
Spindle fibers are composed of microtubules, which are long, hollow tubes made of tubulin proteins. These microtubules are nucleated at the centrosomes, which are organelles located near the nucleus, and radiate outward towards the cell periphery. During cell division, the spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes at the centromere, a specialized region near the center of each chromosome. This attachment allows the spindle fibers to manipulate the movement of the chromosomes during cell division.
1. Chromosome Separation
One of the primary functions of spindle fibers is to separate the chromosomes during cell division. The spindle fibers attach to the centromere of each chromosome and use their dynamic properties to move the chromosomes towards opposite poles of the cell. This process ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes.

2. Chromosome Alignment
Before chromosomes can be separated, they must be properly aligned at the metaphase plate, a region near the center of the cell. Spindle fibers play a crucial role in this process by interacting with the chromosomes and aligning them in a specific order. This ensures that each chromosome is properly attached to the spindle fibers and is ready for separation.
The Role of Microtubules in Chromosome Alignment
Microtubules are the building blocks of spindle fibers, and they play a key role in chromosome alignment. Microtubules are dynamic structures that can grow or shrink depending on the availability of tubulin proteins. During chromosome alignment, microtubules interact with the chromosomes and help to position them at the metaphase plate.

3. Cell Cycle Regulation
Spindle fibers also play a role in regulating the cell cycle. The attachment of spindle fibers to the centromere of each chromosome helps to trigger the transition from metaphase to anaphase. Additionally, the separation of chromosomes during anaphase helps to trigger the transition from anaphase to telophase.
The Role of Spindle Checkpoint in Cell Cycle Regulation
The spindle checkpoint is a quality control mechanism that ensures that chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle fibers before the cell proceeds with cell division. If chromosomes are not properly attached, the spindle checkpoint can delay cell division until the problem is corrected.

4. Cytokinesis
Spindle fibers also play a role in cytokinesis, the process of cell division that results in the physical separation of the cytoplasm. The separation of chromosomes during anaphase helps to trigger the formation of the cleavage furrow, a groove that forms in the cell membrane and helps to separate the cytoplasm.
The Role of Microtubules in Cytokinesis
Microtubules also play a role in cytokinesis by interacting with the actin cytoskeleton and helping to regulate the formation of the cleavage furrow.

5. Error Correction
Finally, spindle fibers play a role in error correction during cell division. The spindle checkpoint helps to ensure that chromosomes are properly attached to the spindle fibers before the cell proceeds with cell division. If chromosomes are not properly attached, the spindle checkpoint can delay cell division until the problem is corrected.
The Importance of Error Correction in Cell Division
Error correction is crucial during cell division to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. Without error correction, cells may receive an incorrect number of chromosomes, leading to genetic disorders or cancer.

In conclusion, spindle fibers play a vital role in cell division, impacting chromosome separation, alignment, cell cycle regulation, cytokinesis, and error correction. The dynamic properties of microtubules, the building blocks of spindle fibers, allow them to interact with chromosomes and regulate their movement during cell division.
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive understanding of the role of spindle fibers in cell division. If you have any questions or comments, please feel free to share them below.
What is the function of spindle fibers during cell division?
+Spindle fibers play a crucial role in cell division, impacting chromosome separation, alignment, cell cycle regulation, cytokinesis, and error correction.
What is the role of microtubules in spindle fibers?
+Microtubules are the building blocks of spindle fibers and play a key role in chromosome alignment and separation during cell division.
What is the importance of error correction in cell division?
+Error correction is crucial during cell division to ensure that each daughter cell receives a complete set of chromosomes. Without error correction, cells may receive an incorrect number of chromosomes, leading to genetic disorders or cancer.