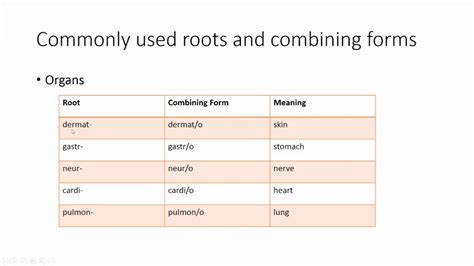
Understanding how words are formed is crucial in building a robust vocabulary. One effective way to decipher unfamiliar words is by recognizing their components, particularly the combination of word roots, prefixes, and suffixes. This combination is known as a combining form, which is a key element in constructing medical and scientific terminology.
When we combine a word root with a prefix or suffix, we create a new word that conveys a specific meaning. Let's dive into the world of word formation and explore how combining forms work.
Word Roots
A word root is the core part of a word that carries the primary meaning. It is the foundation upon which prefixes and suffixes are added to form new words. Word roots are often derived from ancient languages such as Greek and Latin.
For example, the word root "card" means "heart," and it is the core part of words like "cardiac" and "cardiology."

Prefixes
A prefix is a letter or group of letters added to the beginning of a word root to modify its meaning. Prefixes can indicate a range of relationships, such as location, time, or manner.
For instance, the prefix "meta-" means "beyond" or "transcending," and when added to the word root "morph," it forms the word "metamorphosis," meaning a transformation beyond the ordinary.

Suffixes
A suffix is a letter or group of letters added to the end of a word root to modify its meaning or function. Suffixes can indicate a range of relationships, such as possession, agency, or condition.
For example, the suffix "-logy" means "study of" or "science of," and when added to the word root "biolog," it forms the word "biology," meaning the study of living organisms.

Combining Forms
When we combine a word root with a prefix or suffix, we create a new word that conveys a specific meaning. This combination is known as a combining form.
For instance, the combining form "tele-" (meaning "far") plus the word root "vision" forms the word "television," meaning the transmission of visual images over long distances.

Benefits of Understanding Combining Forms
Understanding combining forms has numerous benefits, including:
- Improved vocabulary: Recognizing combining forms can help you decipher unfamiliar words and expand your vocabulary.
- Enhanced comprehension: By understanding the components of words, you can better comprehend their meanings and relationships.
- Effective communication: Using combining forms can help you communicate more precisely and accurately in various fields, including medicine, science, and technology.
Common Combining Forms
Here are some common combining forms, along with their meanings and examples:
- Tele- (meaning "far"): telephone, television, telepathy
- Meta- (meaning "beyond" or "transcending"): metamorphosis, metaphysics, metadata
- Bio- (meaning "life" or "living organisms"): biology, biotechnology, biochemistry
- Neuro- (meaning "nerve" or "nervous system"): neuroscience, neurology, neuroplasticity
- Geo- (meaning "earth" or "geography"): geology, geography, geopolitics

Conclusion
In conclusion, combining forms are a powerful tool for building vocabulary and understanding complex words. By recognizing the combination of word roots, prefixes, and suffixes, you can decipher unfamiliar words and communicate more effectively in various fields. Remember, understanding combining forms is a skill that can be developed with practice and patience, and it can greatly enhance your language abilities.
Share Your Thoughts
Have you ever struggled to understand complex words or terminology? How do you think combining forms can help you improve your vocabulary and communication skills? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below!
FAQs
What is a combining form?
+A combining form is a combination of a word root with a prefix or suffix that conveys a specific meaning.
What are the benefits of understanding combining forms?
+Understanding combining forms can improve vocabulary, enhance comprehension, and facilitate effective communication in various fields.
How can I learn more about combining forms?
+You can learn more about combining forms by studying word roots, prefixes, and suffixes, and practicing vocabulary building exercises.