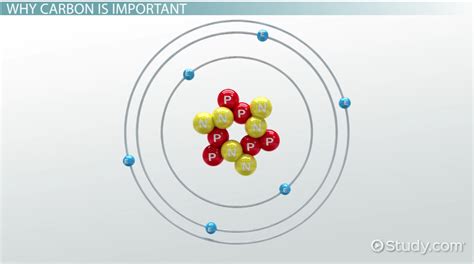
The carbon atom is one of the most fascinating elements in the periodic table, and its ability to form bonds is the key to its incredible versatility. Carbon's unique properties allow it to form a wide variety of compounds, from simple molecules like methane and carbon dioxide to complex biomolecules like proteins and DNA. In this article, we'll explore the different types of bonds that carbon can form and what makes them possible.
The Basics of Carbon Bonding
Carbon has six electrons in its outermost energy level, which is known as the valence shell. This means that carbon has four valence electrons, which are the electrons that participate in bonding with other atoms. Carbon's four valence electrons are arranged in a tetrahedral shape, which allows carbon to form bonds with other atoms in a wide range of orientations.
Types of Carbon Bonds

Carbon can form several types of bonds, including sigma (σ) bonds, pi (π) bonds, and metallic bonds. Sigma bonds are the strongest type of covalent bond and are formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons. Pi bonds are weaker than sigma bonds and are formed when two atoms share two pairs of electrons. Metallic bonds are a type of bond that occurs between metal atoms and are characterized by a "sea" of electrons that surrounds the metal ions.
Carbon-Carbon Bonds
Carbon-carbon bonds are a type of covalent bond that occurs between two carbon atoms. These bonds are incredibly strong and are the foundation of many organic compounds. There are several types of carbon-carbon bonds, including single bonds, double bonds, and triple bonds.
- Single bonds: Single bonds are the simplest type of carbon-carbon bond and are formed when two carbon atoms share a pair of electrons.
- Double bonds: Double bonds are formed when two carbon atoms share two pairs of electrons. These bonds are stronger than single bonds and are characterized by a planar, unsaturated structure.
- Triple bonds: Triple bonds are the strongest type of carbon-carbon bond and are formed when two carbon atoms share three pairs of electrons.
Carbon-Hydrogen Bonds
Carbon-hydrogen bonds are another type of covalent bond that occurs between carbon and hydrogen atoms. These bonds are relatively weak compared to carbon-carbon bonds but are still incredibly important in organic chemistry.
- Single bonds: Single bonds are the simplest type of carbon-hydrogen bond and are formed when a carbon atom shares a pair of electrons with a hydrogen atom.
- Double bonds: Double bonds are not typically formed between carbon and hydrogen atoms, as hydrogen has only one valence electron.
Carbon-Oxygen Bonds
Carbon-oxygen bonds are a type of covalent bond that occurs between carbon and oxygen atoms. These bonds are relatively strong and are characterized by a polar, covalent structure.
- Single bonds: Single bonds are the simplest type of carbon-oxygen bond and are formed when a carbon atom shares a pair of electrons with an oxygen atom.
- Double bonds: Double bonds are formed when a carbon atom shares two pairs of electrons with an oxygen atom.
Factors That Affect Carbon Bond Formation

There are several factors that can affect the formation of carbon bonds, including electronegativity, hybridization, and steric hindrance.
- Electronegativity: Electronegativity is the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a covalent bond. Carbon has a relatively low electronegativity, which allows it to form bonds with a wide range of other atoms.
- Hybridization: Hybridization is the process by which carbon's valence electrons are rearranged to form bonds with other atoms. Carbon's tetrahedral shape allows it to form bonds in a wide range of orientations.
- Steric hindrance: Steric hindrance is the phenomenon by which the physical structure of a molecule can affect its reactivity. Carbon's small size and tetrahedral shape allow it to form bonds in a wide range of orientations, but steric hindrance can still affect the formation of certain bonds.
Conclusion: The Most Likely Formation of Carbon Atom Bonds
The most likely formation of carbon atom bonds is dependent on the specific circumstances of the reaction. However, in general, carbon-carbon bonds are the strongest and most stable type of bond that carbon can form. Carbon-hydrogen bonds and carbon-oxygen bonds are also relatively strong and are incredibly important in organic chemistry.
By understanding the different types of bonds that carbon can form, as well as the factors that affect bond formation, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the incredible versatility of the carbon atom.
Final Thoughts
We hope this article has provided a comprehensive overview of the different types of bonds that carbon can form. Whether you're a student of chemistry or simply interested in learning more about the building blocks of life, understanding carbon bonding is essential for appreciating the incredible complexity and diversity of the natural world.
If you have any questions or would like to learn more about a specific topic related to carbon bonding, please don't hesitate to ask! We'd love to hear from you and continue the conversation.
What is the most common type of carbon bond?
+The most common type of carbon bond is the carbon-carbon single bond.
What is the strongest type of carbon bond?
+The strongest type of carbon bond is the carbon-carbon triple bond.
What is the main factor that affects carbon bond formation?
+The main factor that affects carbon bond formation is electronegativity.