The world of taxes can be overwhelming, especially with the numerous forms and documents required for filing. One such form that often raises questions is the 1040 B Form, also known as the Interest and Dividend Income Statement. In this article, we will delve into the essential facts about the 1040 B Form, its purpose, and how it affects your tax return.

What is the 1040 B Form?
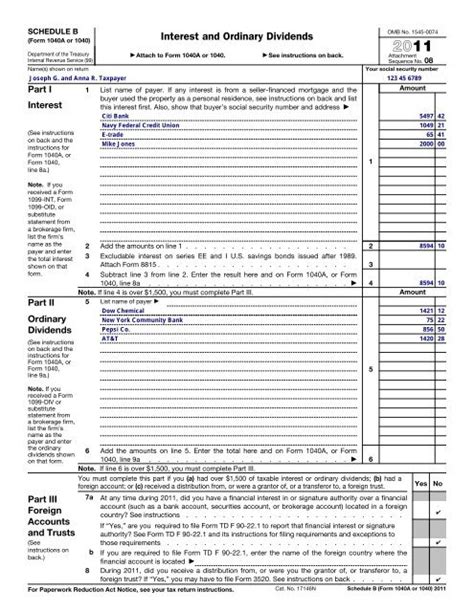
The 1040 B Form is a statement of interest and dividend income, which is a part of the individual income tax return, Form 1040. It is used to report the interest and dividend income earned from various sources, such as banks, investment accounts, and dividend-paying stocks. This form is a crucial component of the tax return, as it helps the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to calculate the taxpayer's total income and determine their tax liability.
Purpose of the 1040 B Form
The primary purpose of the 1040 B Form is to report interest and dividend income earned during the tax year. This form is used to:
- Report interest income from banks, savings accounts, and other financial institutions
- Report dividend income from stocks, mutual funds, and other investment accounts
- Calculate the total interest and dividend income earned during the tax year
- Determine the tax liability on the reported interest and dividend income
Who Needs to File the 1040 B Form?
Not everyone needs to file the 1040 B Form. Typically, taxpayers who have earned interest and dividend income from various sources during the tax year are required to file this form. This includes:
- Individuals with interest income exceeding $1,500 from all sources
- Individuals with dividend income exceeding $1,500 from all sources
- Taxpayers who have received a Form 1099-INT or Form 1099-DIV from a payer
How to Complete the 1040 B Form
Completing the 1040 B Form requires gathering information from various sources, including:
- Form 1099-INT: Statement of Interest Income
- Form 1099-DIV: Statement of Dividend Income
- Bank statements and investment account statements
The form consists of several sections, including:
- Part I: Interest Income
- Part II: Dividend Income
- Part III: Total Interest and Dividend Income
Taxpayers must accurately report their interest and dividend income in the respective sections and calculate the total income earned during the tax year.
Benefits of Filing the 1040 B Form
Filing the 1040 B Form provides several benefits, including:
- Accurate reporting of interest and dividend income
- Calculation of tax liability on reported income
- Potential reduction in tax liability due to deductions and exemptions
- Compliance with IRS regulations and requirements
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When filing the 1040 B Form, taxpayers should avoid common mistakes, such as:
- Failing to report all interest and dividend income
- Incorrectly calculating total interest and dividend income
- Not attaching required documentation, such as Form 1099-INT and Form 1099-DIV
Consequences of Not Filing the 1040 B Form
Failure to file the 1040 B Form or accurately report interest and dividend income can result in:
- Delayed or denied tax refunds
- Penalties and fines imposed by the IRS
- Interest charges on unpaid taxes
- Potential audit or examination by the IRS
Best Practices for Filing the 1040 B Form
To ensure accurate and timely filing of the 1040 B Form, taxpayers should:
- Gather all required documentation and information
- Use tax preparation software or consult a tax professional
- Review and verify the accuracy of the form before submission
- File the form electronically or by mail, as required by the IRS
In conclusion, the 1040 B Form is an essential component of the individual income tax return, requiring accurate reporting of interest and dividend income. By understanding the purpose, requirements, and benefits of filing this form, taxpayers can ensure compliance with IRS regulations and avoid potential consequences.
We hope this article has provided you with valuable insights into the 1040 B Form. If you have any questions or concerns, please feel free to comment below or share this article with others who may find it helpful.
What is the purpose of the 1040 B Form?
+The primary purpose of the 1040 B Form is to report interest and dividend income earned during the tax year.
Who needs to file the 1040 B Form?
+Typically, taxpayers who have earned interest and dividend income from various sources during the tax year are required to file this form.
What are the consequences of not filing the 1040 B Form?
+Failure to file the 1040 B Form or accurately report interest and dividend income can result in delayed or denied tax refunds, penalties, and fines imposed by the IRS.