The world of chemistry is full of fascinating concepts, and one of the most interesting is the formation of ions. In this article, we will delve into the world of negative ions, specifically exploring the elements most likely to form a negative ion.
In chemistry, ions are atoms or molecules that have gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge. Negative ions, also known as anions, are formed when an atom or molecule gains one or more electrons. This process is known as electron gain or reduction.
Understanding Electron Gain and the Formation of Negative Ions

Electron gain occurs when an atom or molecule has a high tendency to attract electrons. This is typically seen in elements with a high electronegativity value. Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond. The higher the electronegativity value, the more likely an element is to form a negative ion.
Factors Influencing the Formation of Negative Ions
Several factors influence the formation of negative ions, including:
- Electronegativity: As mentioned earlier, elements with high electronegativity values are more likely to form negative ions.
- Atomic size: Smaller atoms tend to have a higher electronegativity value and are more likely to form negative ions.
- Electron configuration: Atoms with a nearly full outer energy level are more likely to gain electrons and form a negative ion.
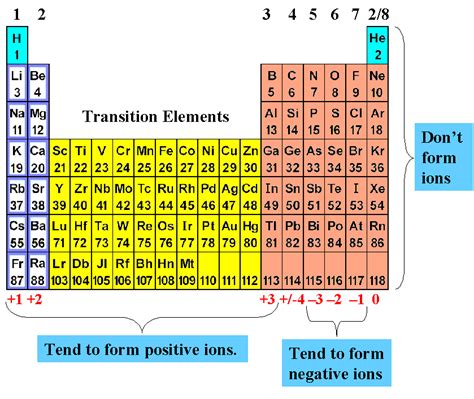
Elements Most Likely to Form a Negative Ion

Based on their electronegativity values, atomic size, and electron configuration, the following elements are most likely to form a negative ion:
- Fluorine (F): With an electronegativity value of 4.0, fluorine is the most electronegative element and is highly likely to form a negative ion.
- Chlorine (Cl): Chlorine has an electronegativity value of 3.5 and is often found as a negative ion in compounds.
- Bromine (Br): With an electronegativity value of 3.3, bromine is also commonly found as a negative ion.
- Iodine (I): Iodine has an electronegativity value of 3.1 and is often used in the formation of negative ions.
- Oxygen (O): Oxygen has an electronegativity value of 3.5 and is commonly found as a negative ion in compounds such as oxides and hydroxides.
Other Elements That Can Form Negative Ions
While the elements listed above are the most likely to form negative ions, other elements can also form negative ions under certain conditions. These include:
- Nitrogen (N): Nitrogen can form a negative ion in compounds such as nitrides and azides.
- Phosphorus (P): Phosphorus can form a negative ion in compounds such as phosphides and phosphates.
- Sulfur (S): Sulfur can form a negative ion in compounds such as sulfides and sulfates.
Conclusion and Future Research Directions

In conclusion, the formation of negative ions is an important concept in chemistry, and understanding the elements most likely to form negative ions is crucial. The elements listed above, particularly fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, and oxygen, are the most likely to form negative ions due to their high electronegativity values and electron configuration.
Future research directions in this area may include:
- Exploring the properties of negative ions: Further research is needed to understand the properties of negative ions and their behavior in different environments.
- Developing new compounds: Researchers may explore the development of new compounds that utilize negative ions, potentially leading to new materials and applications.
Encouraging Engagement and Further Learning
We hope this article has provided you with a comprehensive understanding of the elements most likely to form a negative ion. If you have any questions or would like to learn more about this topic, please leave a comment below. Share this article with your friends and colleagues to spark interesting discussions and debates.
FAQ Section:
What is an ion?
+An ion is an atom or molecule that has gained or lost electrons, resulting in a net positive or negative charge.
What is electronegativity?
+Electronegativity is a measure of an atom's ability to attract electrons in a covalent bond.
What are some common negative ions?
+Common negative ions include fluoride (F-), chloride (Cl-), bromide (Br-), iodide (I-), and oxide (O2-).